Coding Strand Template Strand Mrna
Coding Strand Template Strand Mrna - Web the coding strand and template strand in translation. The coding strand turns gray and then disappears, leaving the template strand (see strands above). It is presented in the 5' to 3' direction. Web transcription uses one of the two exposed dna strands as a template; Web translates dna or mrna to the other and a protein strand (amino acids). Web this strand is called the coding strand as its sequence corresponds directly to the mrna sequence. Web the main difference between template and coding strand is that template strand only serves as the template for transcription whereas coding strand contains the exact same sequence of nucleotides in the mrna except thymine. They help in the formation of mrna. The coding strand has a complementary nucleotide sequence. The template strand is the one that rna polymerase uses as the basis to build the rna. The template strand is the one that rna polymerase uses as the basis to build the rna. Web actually, the mrna strand is coded from the template strand of the dna which runs from 3' to 5' end. Jun 14, 2016 at 21:24. Web the difference between a template and a coding strand is primarily based on two characteristics: They. Most images show 17 base pairs. The template strand is directed in the 5’ to 3’ direction. The template strand is the one that rna polymerase uses as the basis to build the rna. The nontemplate strand is referred to as the coding strand because its sequence will be the same as that of the new rna molecule. Mrna hairpins. In the newly made rna, all of the t. This strand dictates the mrna sequence, aligning with it in a complementary fashion. Web this template strand is called the noncoding strand. The bases are the same, except. This strand is also called the coding strand. For example, if the coding strand reads atg, the mrna reads. Web the template strand, on the other hand, has a sequence of nucleotides that is complementary to the sequence on the coding strand. The coding strand turns gray and then disappears, leaving the template strand (see strands above). Web the coding strand and template strand in translation. The template. Web here, they take part in the transcription. Web transcription is the process of copying a segment of dna into rna. This strand dictates the mrna sequence, aligning with it in a complementary fashion. Figure 1.23 illustrates the point that a gene may be longer than the region coding for the protein because of 5' and/or 3' untranslated regions. Wherever. Web this template strand is called the noncoding strand. Web the strand that reads as the reverse complement of the mrna is the template strand. The coding strand has a complementary nucleotide sequence. The template strand is the one that rna polymerase uses as the basis to build the rna. In the newly made rna, all of the t. A bit like two snakes coiled. The template strand is directed in the 5’ to 3’ direction. Both dna and rna are nucleic acids, which use base pairs of. For example, if the coding strand reads atg, the mrna reads. Web the coding strand and template strand in translation. Web i'll try to answer it. The sense strand is the strand of dna that has the same. Both dna and rna are nucleic acids, which use base pairs of. Web this strand is called the coding strand as its sequence corresponds directly to the mrna sequence. Web translates dna or mrna to the other and a protein strand (amino. Transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand.the mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with the exception that rna contains a uracil (u) in place of the thymine (t) found in dna.during. Web the template strand, on. The sense strand is the strand of dna that has the same. The segments of dna transcribed into rna molecules that can encode proteins produce messenger rna (mrna). Figure 1.22.only one strand of duplex dna codes for a particular product. The coding strand is the other strand of dna helix other than the template strand that runs from 5' to. The nontemplate strand is referred to as the coding strand because its sequence will be the same as that of the new rna molecule. It is presented in the 5' to 3' direction. A bit like two snakes coiled. Most images show 17 base pairs. Web here, they take part in the transcription. Web sometimes the phrases coding strand and template strand are encountered in place of sense and antisense,. The coding strand has a complementary nucleotide sequence. The template strand is directed in the 5’ to 3’ direction. Web i'll try to answer it. Web transcription uses one of the two exposed dna strands as a template; For example, if the coding strand reads atg, the mrna reads. The segments of dna transcribed into rna molecules that can encode proteins produce messenger rna (mrna). Both dna and rna are nucleic acids, which use base pairs of. Web by convention, the coding strand is the strand used when displaying a dna sequence. The coding strand and template strand of dna play crucial roles in this process, guiding the mrna’s formation. Web the difference between a template and a coding strand is primarily based on two characteristics:
IMP Coding (Sense) vs Template (AntiSense) Strands Biology activity
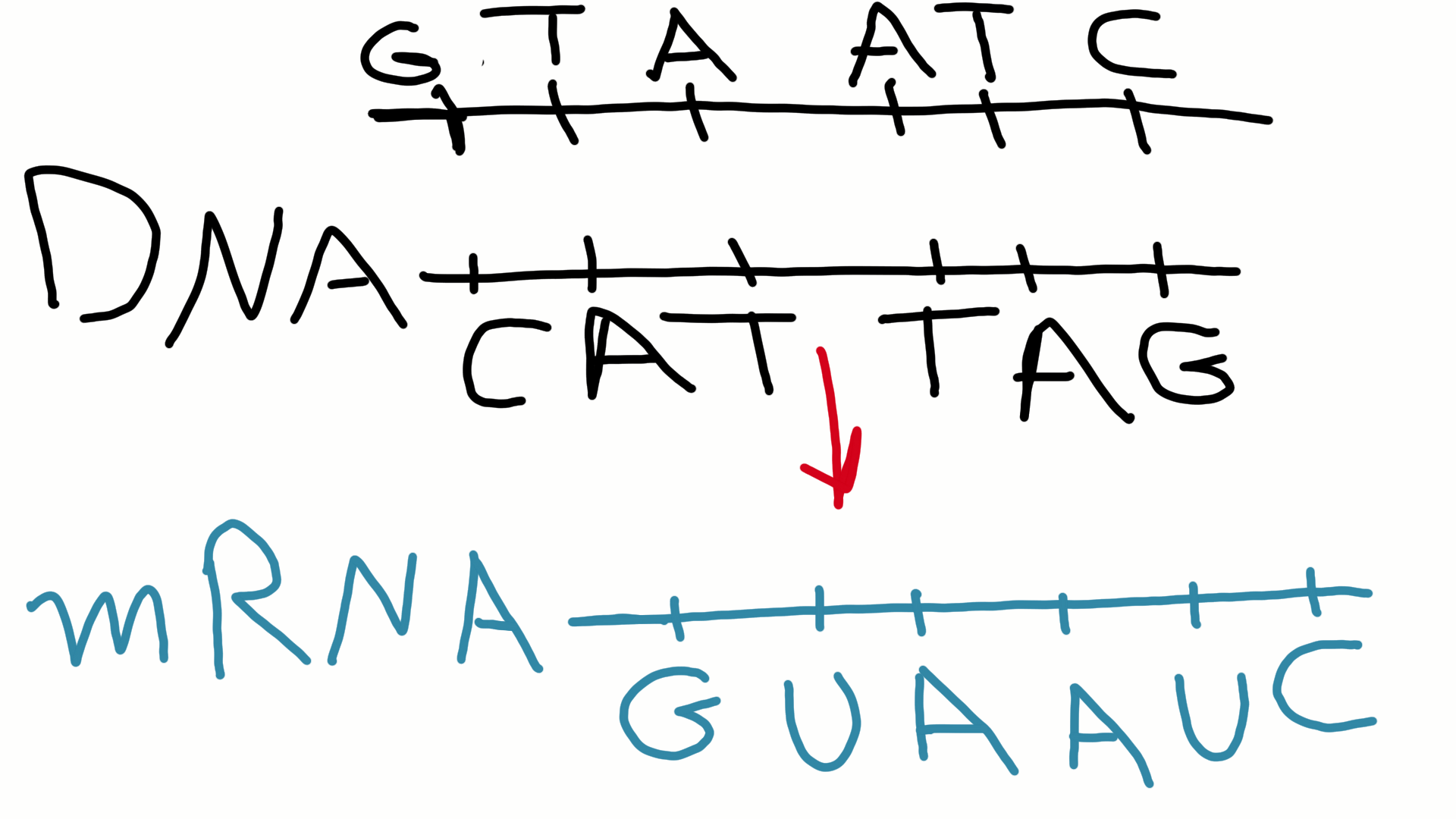
Mrna Template Strand

What Is The Template For Mrna
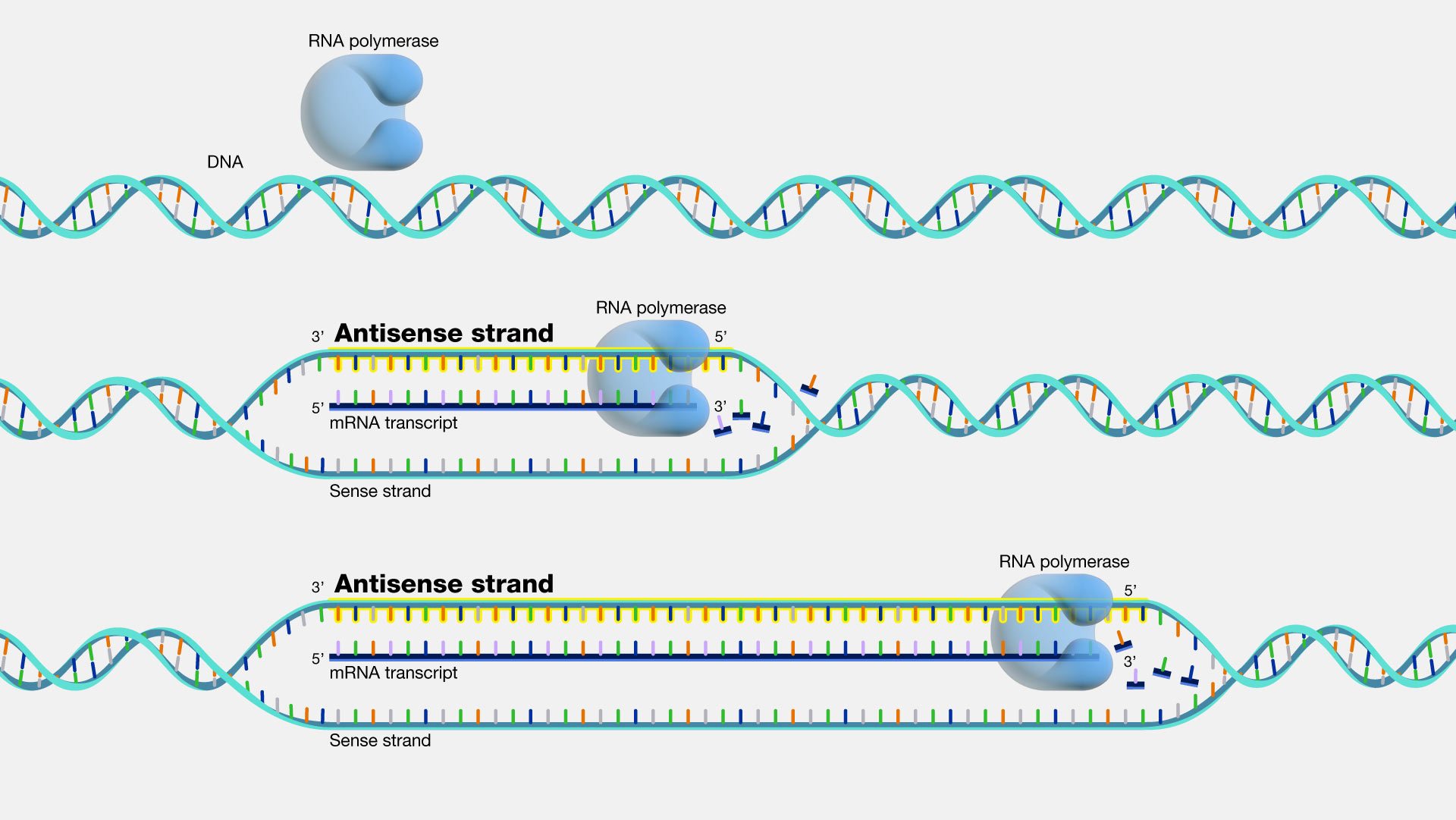
Mrna Template Strand
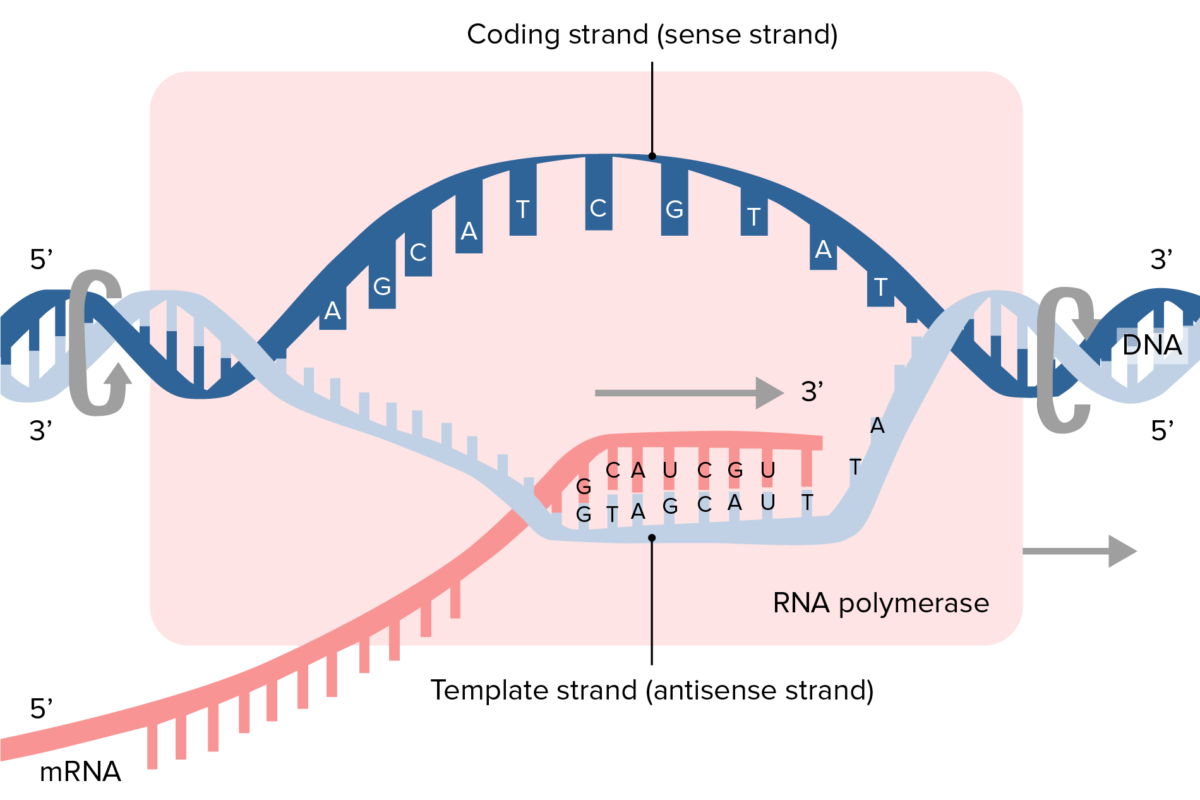
Mrna Template Strand

Template Strand Mrna
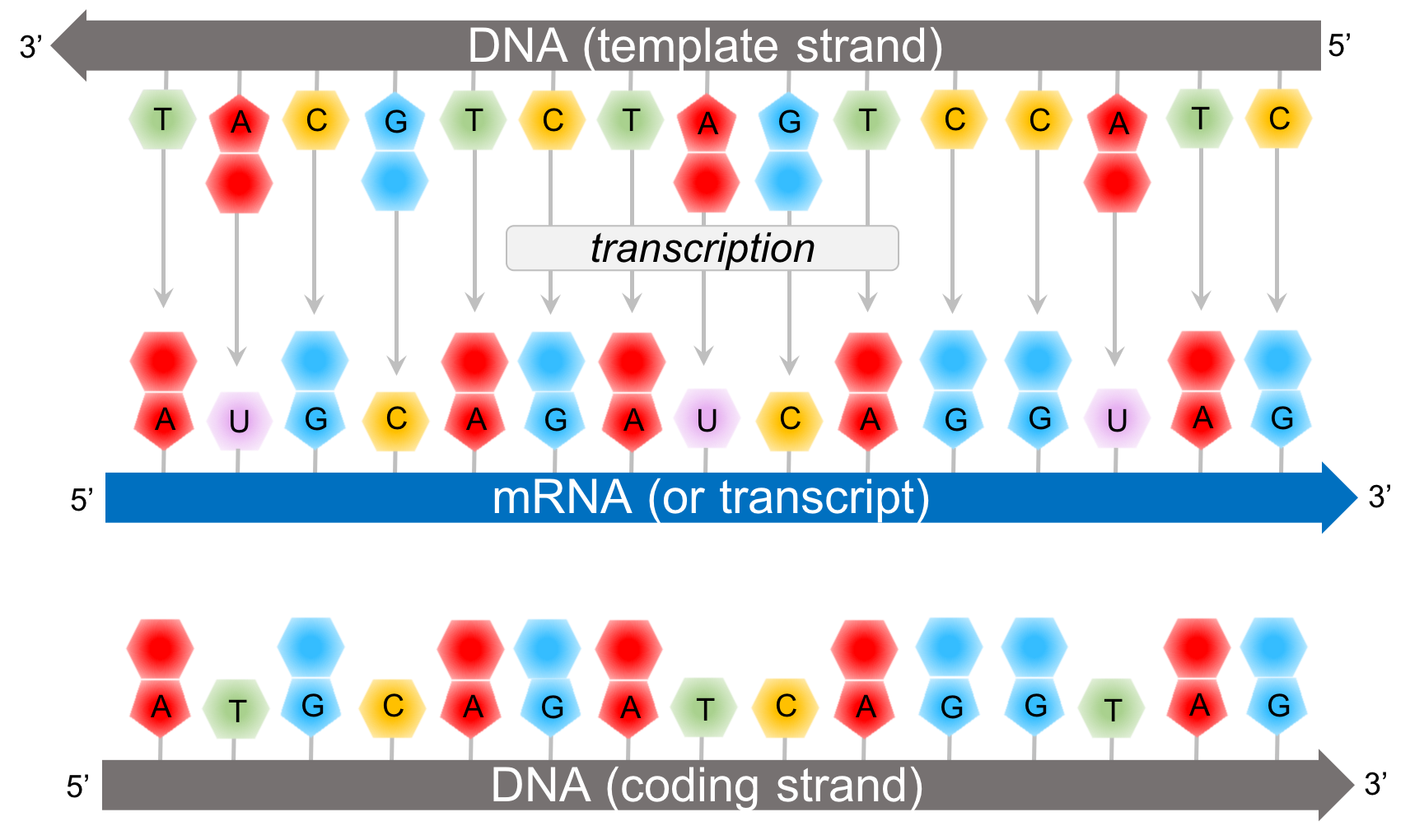
Chapter The Code — The Biology Primer

Coding Strand And Template Strand

Coding Strand vs. Template Strand 6 Key Differences
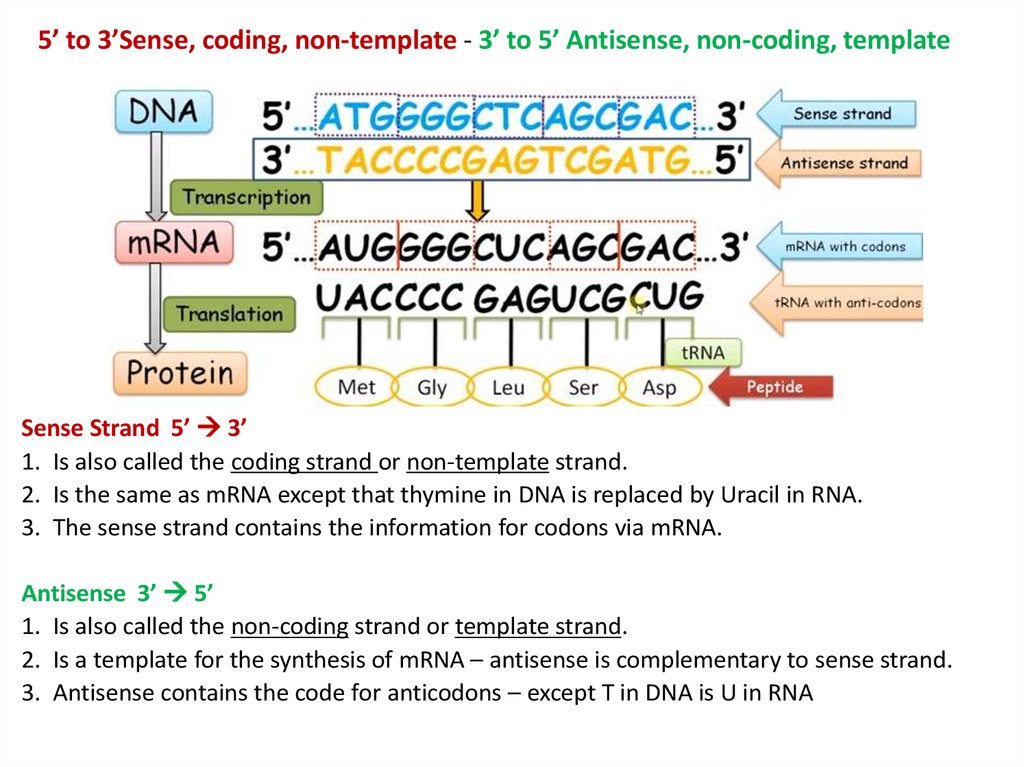
Coding Strand Vs Template Strand
Web Transcription Is The Process Of Copying A Segment Of Dna Into Rna.
Mrna Hairpins Can Be Formed When Two Complementary Sequences In A Single Mrna Molecule Meet And Bind Together, After A Folding Or.
Web The Strand That Reads As The Reverse Complement Of The Mrna Is The Template Strand.
Jun 14, 2016 At 21:24.
Related Post: