Coding Strand Template Strand
Coding Strand Template Strand - This way, both strands work together, ensuring the right information is transferred from dna to rna. The template strand is the one that rna polymerase uses as the basis to build the rna. The template strand serves as a guide during transcription and determines the sequence of the. Web template strand and coding strand refer to the two complementary strands of dna that encode genetic information. Web transcription uses one of the two exposed dna strands as a template; As it reads this template one base at a time, the polymerase builds an rna molecule out of complementary nucleotides, making a chain that grows from 5' to 3'. Web the difference between template and coding strand is mainly due to the following properties: This strand is called the template strand.the rna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate (or coding) strand.however, there is one important difference: Importance in dna replication both the coding strand and the template strand are vital for the process of dna replication, which ensures the accurate duplication of genetic information during. Web actually, the mrna strand is coded from the template strand of the dna which runs from 3' to 5' end. Web the main difference between template and coding strand is that template strand only serves as the template for transcription whereas coding strand contains the exact same sequence of nucleotides in the mrna except thymine. The coding strand is typically located on the 5' to 3' direction, while the template strand is located on the 3' to 5' direction. In. For example, if the coding strand reads atg, the mrna reads. Web the coding strand is directly involved in protein synthesis, while the template strand serves as a template for rna synthesis. Web template strand and coding strand refer to the two complementary strands of dna that encode genetic information. They help in the formation of mrna. In the newly. Web given a dna sequence alone, you can annotate open reading frames (orfs) in order to identify the coding strand, with the caveat that not all orfs are genes. This process ensures that the rna carries the correct information dictated by the genetic code. The template strand is directed in the 5’ to 3’ direction. Web the coding strand serves. Mrna bases are complementary to and bind to dna bases; This process ensures that the rna carries the correct information dictated by the genetic code. They help in the formation of mrna. The template strand is the one that rna polymerase uses as the basis to build the rna. Web by convention, the coding strand is the strand used when. Web and then it shows me a figure, where a promoter sequence is shown in the template strand, with the transcription complex attached. The coding strand and template strand of dna play crucial roles in this process, guiding the mrna’s formation. The coding strand is directed in the 3’ to 5’ direction. Web the template strand, as its name suggests,. Web and then it shows me a figure, where a promoter sequence is shown in the template strand, with the transcription complex attached. The coding strand is directed in the 3’ to 5’ direction. As it reads this template one base at a time, the polymerase builds an rna molecule out of complementary nucleotides, making a chain that grows from. Web given a dna sequence alone, you can annotate open reading frames (orfs) in order to identify the coding strand, with the caveat that not all orfs are genes. A bit like two snakes coiled. As it reads this template one base at a time, the polymerase builds an rna molecule out of complementary nucleotides, making a chain that grows. Web one strand of dna, the template strand, acts as a template for rna polymerase. Importance in dna replication both the coding strand and the template strand are vital for the process of dna replication, which ensures the accurate duplication of genetic information during. The coding strand and template strand of dna play crucial roles in this process, guiding the. The coding strand is the other strand of dna helix other than the template strand that runs from 5' to 3' end and is parallel to the mrna strand. It is presented in the 5' to 3' direction. The coding strand is directed in the 3’ to 5’ direction. Understanding the differences between these two strands is crucial in comprehending. This strand dictates the mrna sequence, aligning with it in a complementary fashion. Web the difference between template and coding strand is mainly due to the following properties: The template strand is directed in the 5’ to 3’ direction. It is presented in the 5' to 3' direction. Mrna bases are complementary to and bind to dna bases; Web the coding strand and the template strand have opposite orientations and are aligned in an antiparallel manner. Web one strand of dna, the template strand, acts as a template for rna polymerase. Web the difference between template and coding strand is mainly due to the following properties: As it reads this template one base at a time, the polymerase builds an rna molecule out of complementary nucleotides, making a chain that grows from 5' to 3'. Web by convention, the coding strand is the strand used when displaying a dna sequence. This process ensures that the rna carries the correct information dictated by the genetic code. The coding strand and template strand of dna play crucial roles in this process, guiding the mrna’s formation. In the newly made rna, all of the t. They help in the formation of mrna. For example, if the coding strand reads atg, the mrna reads. Web the main difference between template and coding strand is that template strand only serves as the template for transcription whereas coding strand contains the exact same sequence of nucleotides in the mrna except thymine. Web the coding strand of each dsrna has a single orf, except for seg11 and seg12 of rdv (table 28 ), seg9 of rice gall dwarf virus (rgdv) and seg9 of wtv. Web the coding strand and template strand in translation. Web actually, the mrna strand is coded from the template strand of the dna which runs from 3' to 5' end. Importance in dna replication both the coding strand and the template strand are vital for the process of dna replication, which ensures the accurate duplication of genetic information during. The coding strand is typically located on the 5' to 3' direction, while the template strand is located on the 3' to 5' direction.
Template and coding strand targeting of spacers. A Schematic

Information Flow and Levels of Regulation Medical 1st Ed
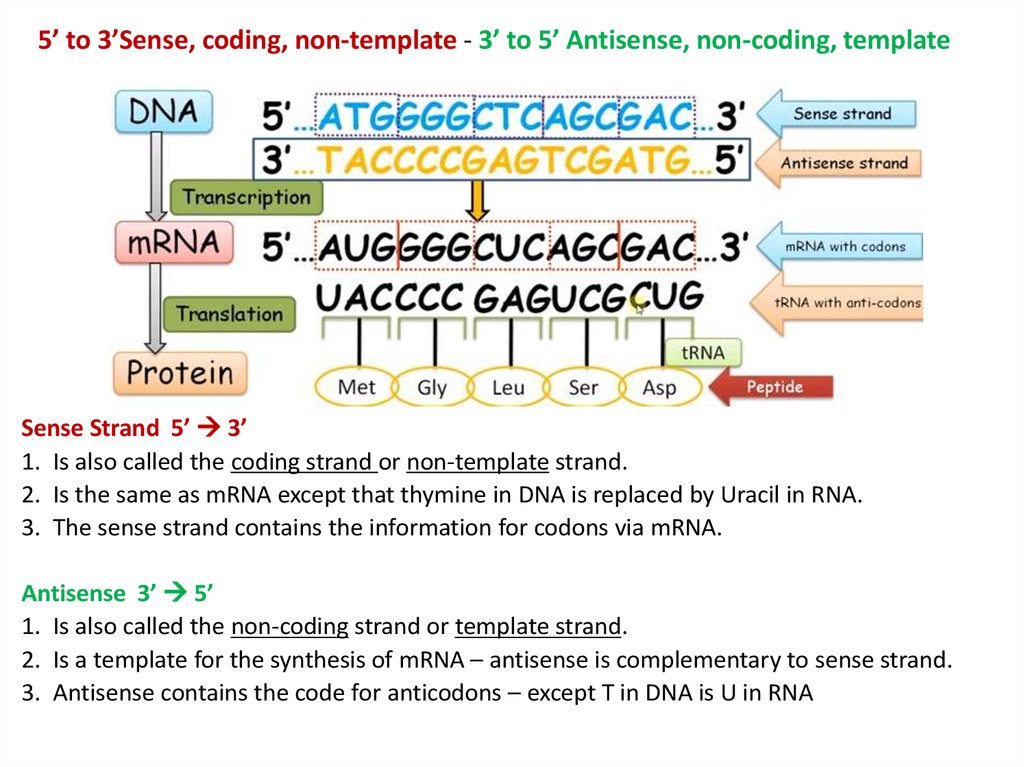
Template Strand And Coding Strand
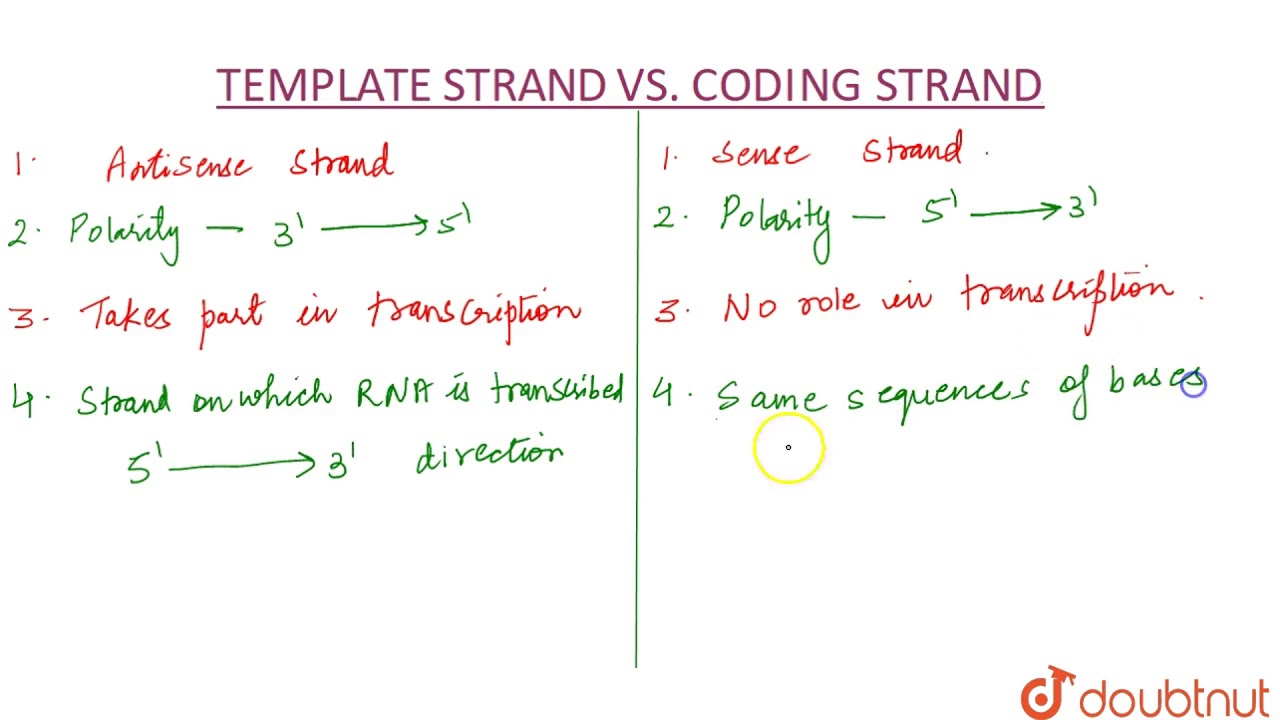
Template Strand And Coding Strand

Template and coding strands of DNA YouTube

Coding Strand And Template Strand
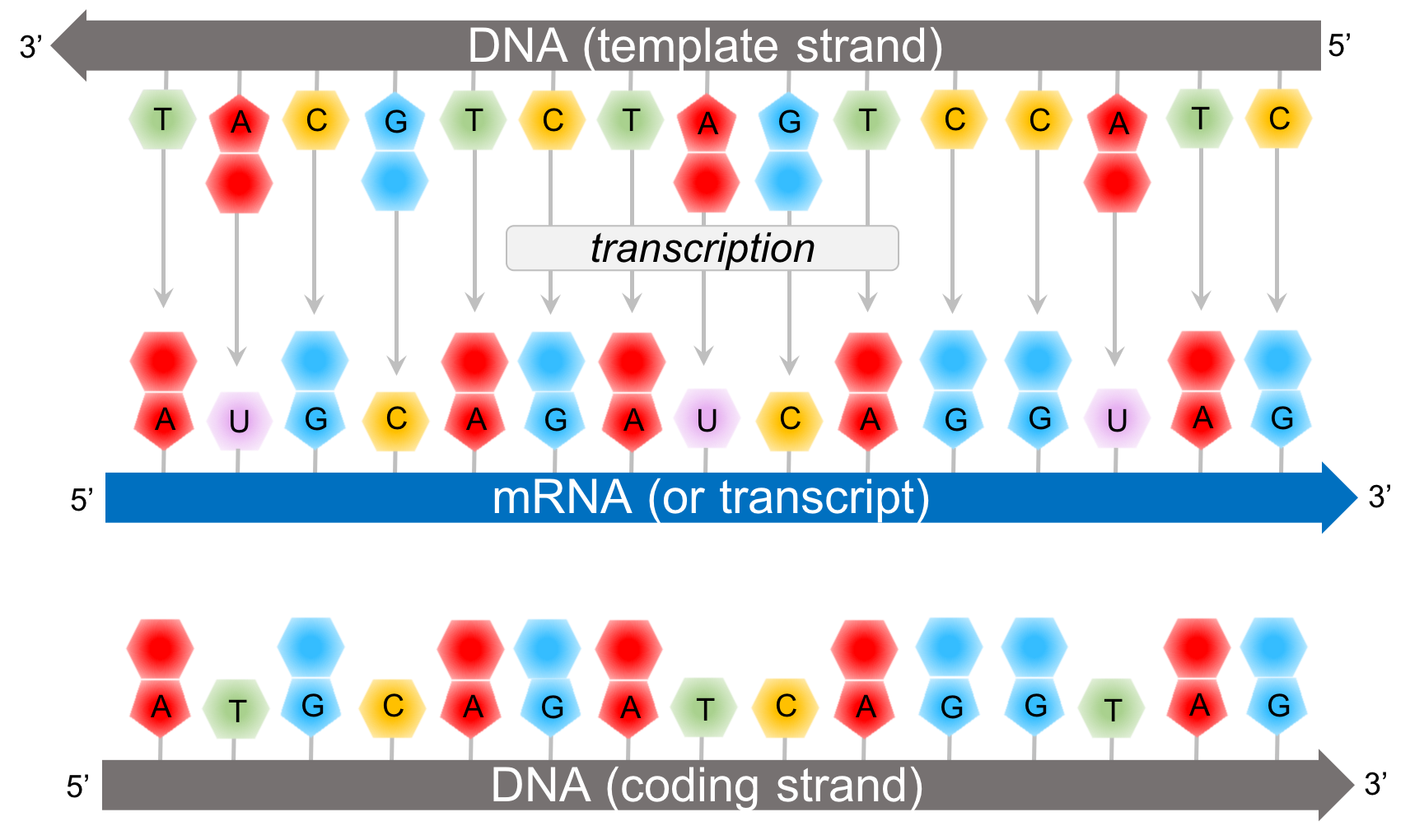
Chapter The Code — The Biology Primer

Coding Strand vs. Template Strand 6 Key Variations sciencesavers

Coding Versus Template Strand

Dna Template Strand And Coding Strand
Web In The Dna Molecule, The Coding Strand And The Template Strand Differ In Their Bases’ Sequence.
Web The Template Strand, On The Other Hand, Has A Sequence Of Nucleotides That Is Complementary To The Sequence On The Coding Strand.
The Coding Strand Has A Complementary Base Sequence To The Template Strand, Except For Thymine (T) Being Replaced By Uracil (U) In Rna.
Mrna Bases Are Complementary To And Bind To Dna Bases;
Related Post: