Coding Template Strand
Coding Template Strand - The coding strand moves in the 5′ to 3′ direction, opposite to the template strand and it contains sequences that are complementary to the template. 37k views 3 years ago. Its counterpart, the antisense strand, guides the creation of a complementary rna strand during transcription. Web the template strand: Complementary to the coding strand, the template strand acts as the original blueprint. Adhering to the strict rules of base pairing, adenine aligns with thymine, and guanine with cytosine. Web the nontemplate strand is referred to as the coding strand because its sequence will be the same as that of the new rna molecule. In most organisms, the strand of dna that. One strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary rna transcript. When it comes to understanding the intricacies of dna and rna, two important concepts to grasp are the coding strand and the template. Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. The template strand is usually directed 3’ to. Web the template strand is the one that rna polymerase uses as the basis to build the rna. Web the coding strand is the template strand (it's also called the sense or transcribed strand). It contains complementary nucleotide sequences to the transcribed mrna. One strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary rna transcript. Complementary to the coding strand, the template strand acts as the original blueprint. It contains complementary nucleotide sequences to the transcribed mrna. When it comes to understanding the intricacies of dna and rna, two important concepts to grasp are the coding strand and the. The replacement of thymine (t) in dna with uracil (u) in mrna. Web the strand of dna from which mrna is formed after transcription is known as the template strand or the antisense strand. The coding strand determines the correct nucleotide sequence of mrna. Web transcription is performed by enzymes called rna polymerases, which link nucleotides to form an rna. The template strand is usually directed 3’ to. Given a dna sequence alone, you can annotate open reading frames (orfs) in order to identify the coding strand, with the caveat that. 37k views 3 years ago. During transcription, it guides the synthesis of mrna, ensuring accuracy in the transfer of genetic information. Web one strand of the dna, the template. Given a dna sequence alone, you can annotate open reading frames (orfs) in order to identify the coding strand, with the caveat that. The coding strand determines the correct nucleotide sequence of mrna. Complementary to the coding strand, the template strand acts as the original blueprint. The replacement of thymine (t) in dna with uracil (u) in mrna. 37k views. Adhering to the strict rules of base pairing, adenine aligns with thymine, and guanine with cytosine. Web the strand of dna from which mrna is formed after transcription is known as the template strand or the antisense strand. The coding strand contains the same sequence as the mrna, except for one difference: Web what is the difference between coding strand. When it comes to understanding the intricacies of dna and rna, two important concepts to grasp are the coding strand and the template. As transcription proceeds, rna polymerase traverses the template. In most organisms, the strand of dna that. Web the strand of dna from which mrna is formed after transcription is known as the template strand or the antisense. Web the nontemplate strand is referred to as the coding strand because its sequence will be the same as that of the new rna molecule. Its counterpart, the antisense strand, guides the creation of a complementary rna strand during transcription. Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. As transcription proceeds, rna polymerase traverses the template. During transcription, it. During transcription, it guides the synthesis of mrna, ensuring accuracy in the transfer of genetic information. Adhering to the strict rules of base pairing, adenine aligns with thymine, and guanine with cytosine. Web template strand and coding strand refer to the two complementary strands of dna that encode genetic information. In most organisms, the strand of dna that. The replacement. In most organisms, the strand of dna that. Web transcription is performed by enzymes called rna polymerases, which link nucleotides to form an rna strand (using a dna strand as a template). Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. Web one strand of the dna, the template strand (or noncoding strand), is used as a template for rna. It contains complementary nucleotide sequences to the transcribed mrna. The coding strand moves in the 5′ to 3′ direction, opposite to the template strand and it contains sequences that are complementary to the template. The coding strand contains the same sequence as the mrna, except for one difference: Web what is the difference between coding strand and template strand? Web if this strand is the coding strand, determine the rna and possible amino acid sequence. Web one strand of the dna, the template strand (or noncoding strand), is used as a template for rna synthesis. When referring to dna transcription, the coding strand (or informational strand) is the dna strand whose base. The coding strand is the other strand of dna helix other than the. One strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary rna transcript. Web the nontemplate strand is referred to as the coding strand because its sequence will be the same as that of the new rna molecule. As transcription proceeds, rna polymerase traverses the template. Given a dna sequence alone, you can annotate open reading frames (orfs) in order to identify the coding strand, with the caveat that. Web the template strand: Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. Web the coding strand is the template strand (it's also called the sense or transcribed strand). Adhering to the strict rules of base pairing, adenine aligns with thymine, and guanine with cytosine.
Template Strand And Coding Strand

Coding Strand vs. Template Strand 6 Key Differences
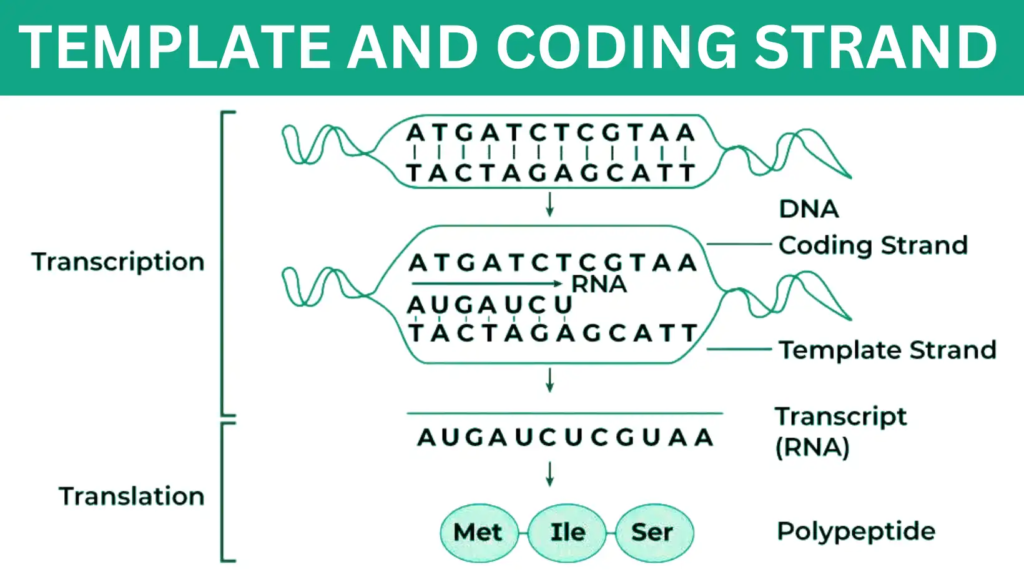
Difference Between Template and Coding Strand

Difference Between Template and Coding Strand Definition

Coding Strand And Template Strand

Template and coding strand targeting of spacers. A Schematic
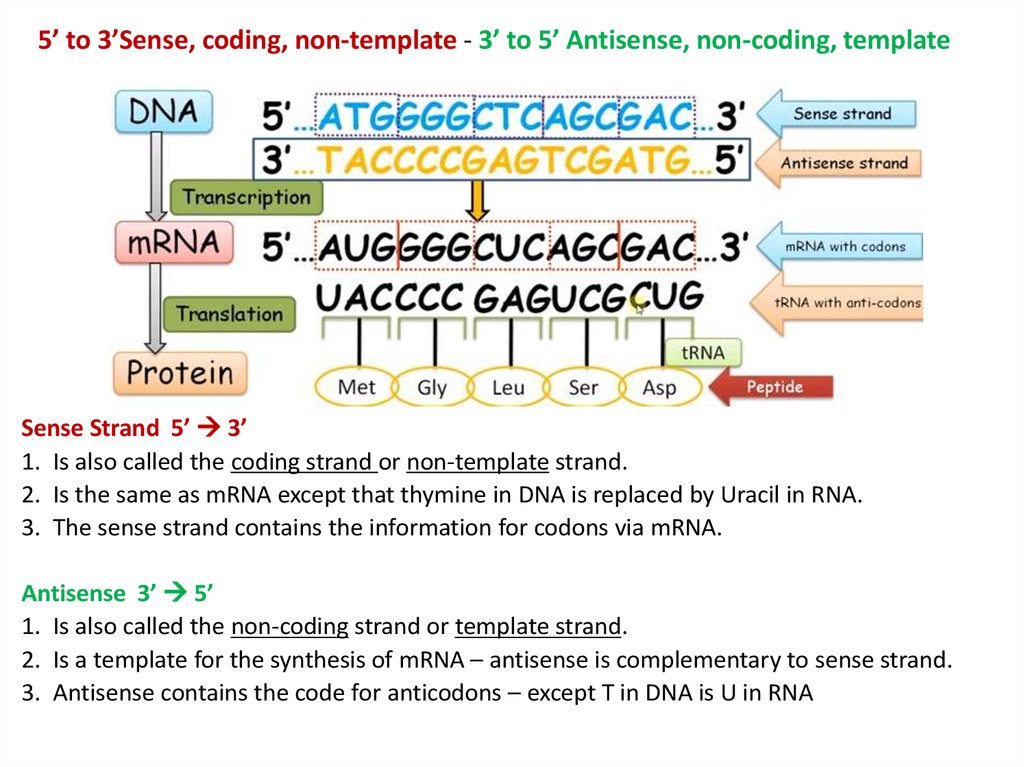
Coding Strand Vs Template Strand

IMP Coding (Sense) vs Template (AntiSense) Strands Biology activity

Template and coding strands of DNA YouTube
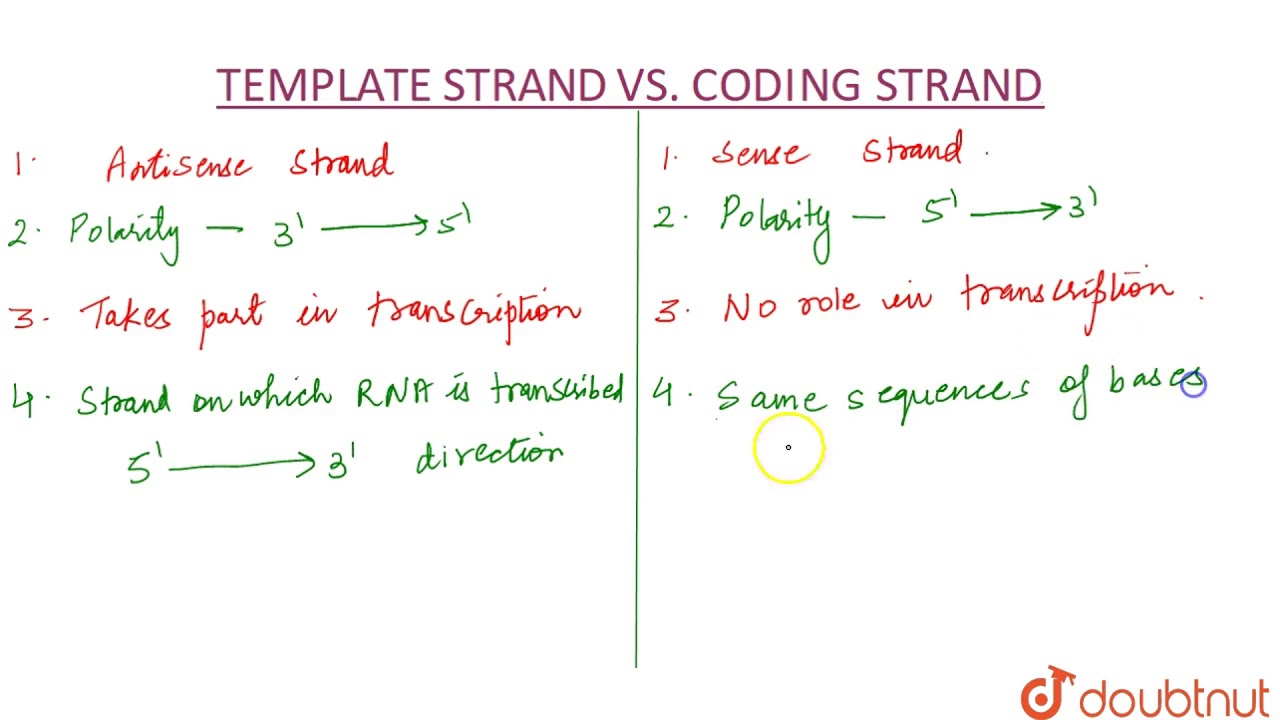
Template Strand And Coding Strand
Web The Strand Of Dna From Which Mrna Is Formed After Transcription Is Known As The Template Strand Or The Antisense Strand.
In Most Organisms, The Strand Of Dna That.
Web The Template Strand Is The One That Rna Polymerase Uses As The Basis To Build The Rna.
37K Views 3 Years Ago.
Related Post: