Dna Template And Coding Strand
Dna Template And Coding Strand - Here is an overview of the central dogma. Translation = rna → protein. The other strand, the coding strand, is identical to the rna transcript in sequence, except that it has uracil (u) bases in place of thymine (t) bases. The coding strand is the other strand of dna helix other than the template strand that runs from 5' to 3' end and is parallel to the mrna strand. Web it is also called (+) strand, or nontemplate strand. The nucleotide at the 5′ end of the chain retains its triphosphate group. An investigator is studying the transcription of dna in a mouse model. Adenine (a) always bonds with thymine (t) and cytosine (c) always bonds with guanine (g). Memory anchors and partner content. The coding strand moves from 5′ to 3′ along the dna molecule. What is dna template strand? This video explain the difference between a. Think of an mrna transcript as a portable gene: Web the answer is simple : The nucleotide at the 5′ end of the chain retains its triphosphate group. Replication relies on complementary base pairing, that is the principle explained by chargaff's rules: 37k views 3 years ago topic 5 expression of biological information. This video explain the difference between a. An investigator is studying the transcription of dna in a mouse model. Web the following is the nucleotide sequence of a dna template strand transcribed by rna polymerase: Understand that within a single piece of dna, either strand can be used as the template for different genes, but the rna will still be produced from 5’ → 3’. What is the difference between coding strand and template strand? Think of an mrna transcript as a portable gene: Replication relies on complementary base pairing, that is the principle explained. What is dna template strand? What is the difference between coding strand and template strand? 37k views 3 years ago topic 5 expression of biological information. The mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with the exception that rna contains a uracil (u) in place of. Web the sense strand is the strand of dna that has the same sequence as the mrna, which takes the antisense strand as its template during transcription, and eventually undergoes (typically, not always) translation into a protein. Web the answer is simple : Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. Dna serves as the template for the synthesis. As transcription proceeds, rna polymerase traverses the template strand and uses base pairing complementarity with the dna template to create an rna copy (which elongates during the traversal). Here is an overview of the central dogma. Dna serves as the template for the synthesis of rna much as it does for its own replication. Memory anchors and partner content. Web. Web the answer is simple : Web actually, the mrna strand is coded from the template strand of the dna which runs from 3' to 5' end. Smaller and more mobile than the dna sequence that it is built from, but containing the same information. One strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary rna. The coding strand serves as a template for producing complementary rna. It acts as the template for rna synthesis, guiding the formation of mrna. Replication relies on complementary base pairing, that is the principle explained by chargaff's rules: The coding strand moves from 5′ to 3′ along the dna molecule. Web position of the template and coding strands during transcription. Adenine (a) always bonds with thymine (t) and cytosine (c) always bonds with guanine (g). One strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary rna transcript. The coding strand is the other strand of dna helix other than the template strand that runs from 5' to 3' end and is parallel to the mrna strand.. The template strand moves in the opposite direction, from 3′ to 5′. One strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary rna transcript. An investigator is studying the transcription of dna in a mouse model. 37k views 3 years ago topic 5 expression of biological information. The template strand runs in. Web it is also called (+) strand, or nontemplate strand. The template strand moves in the opposite direction, from 3′ to 5′. As transcription proceeds, rna polymerase traverses the template strand and uses base pairing complementarity with the dna template to create an rna copy (which elongates during the traversal). Web usmle® step 1 style questions usmle. 42k views 6 years ago dna structure. The coding strand is the other strand of dna helix other than the template strand that runs from 5' to 3' end and is parallel to the mrna strand. The mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with the exception that rna contains a uracil (u) in place of the thymine (t) found in dna. The nucleotide at the 5′ end of the chain retains its triphosphate group. Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. Dna serves as the template for the synthesis of rna much as it does for its own replication. The template strand runs in. One strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary rna transcript. What is dna template strand? When referring to dna transcription, the coding strand (or informational strand) is the dna strand whose base sequence is identical to the base sequence of the rna transcript produced (although with thymine replaced by uracil). (left to right opposites of the letters) click the card to flip 👆. Understand that within a single piece of dna, either strand can be used as the template for different genes, but the rna will still be produced from 5’ → 3’.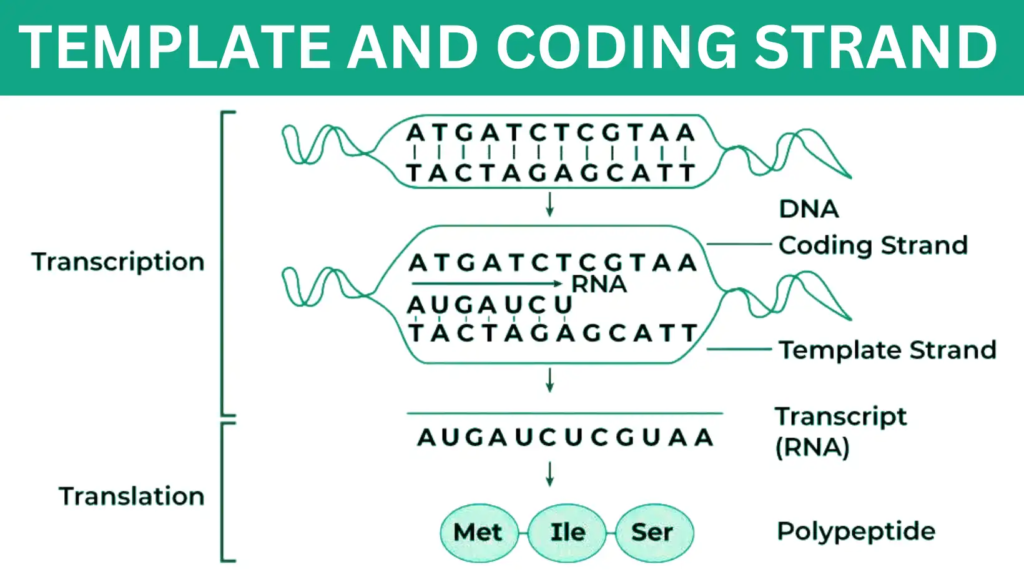
Difference Between Template and Coding Strand

Coding Versus Template Strand During Transcription, Only One Of The Two

Coding Strand vs. Template Strand 6 Key Differences
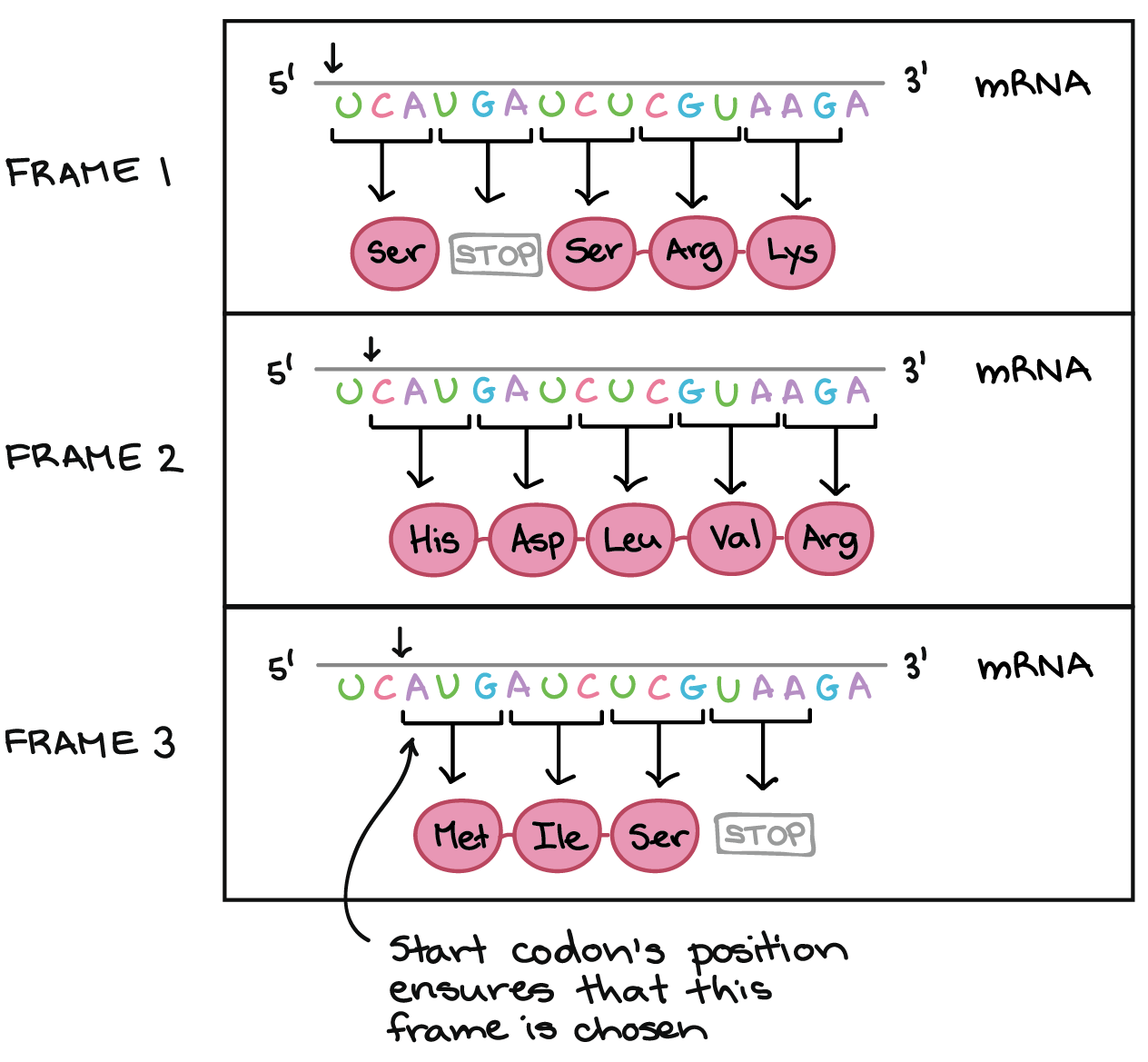
A Codon Consists of a Sequence of How Many Nucleotides
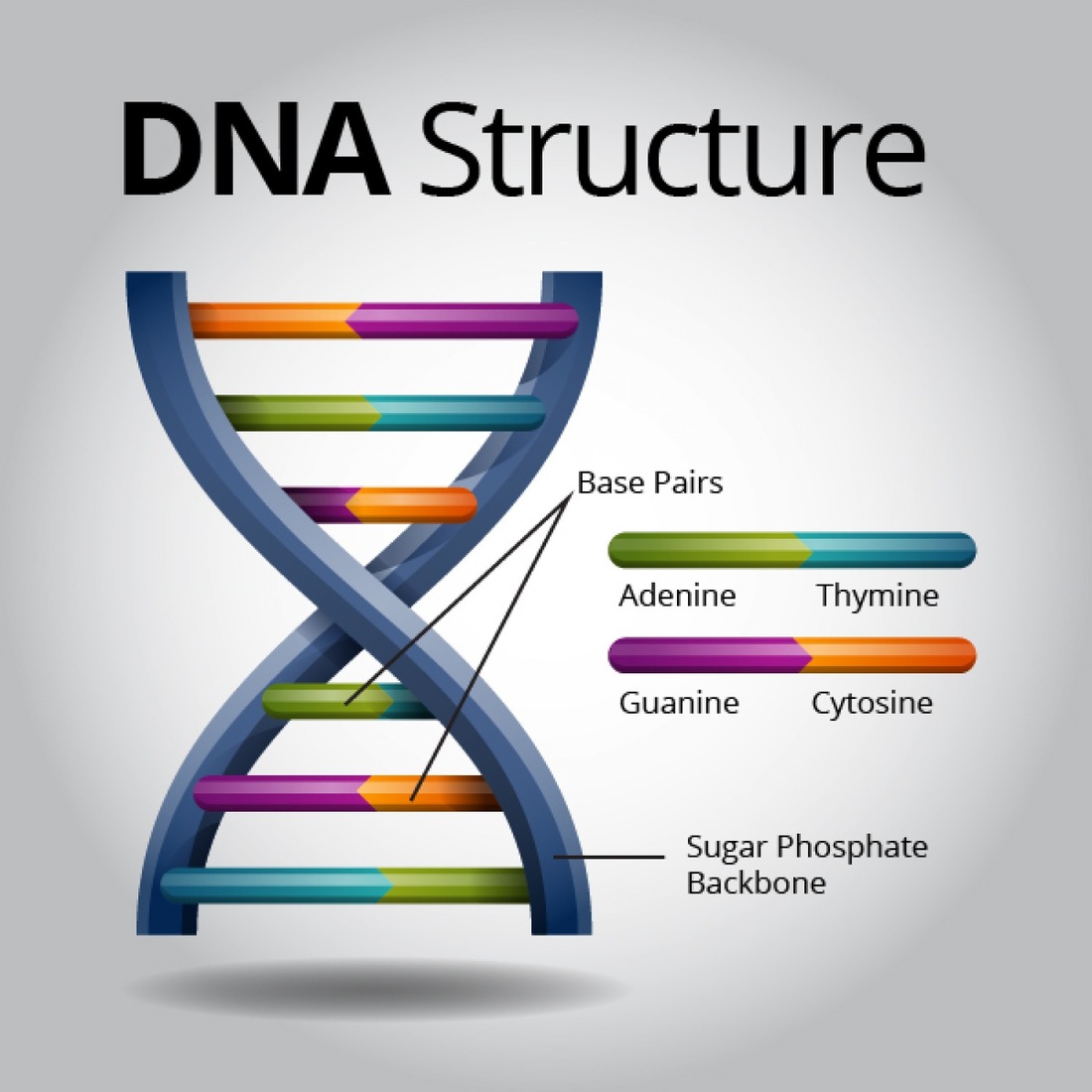
DNA AP Biology Portfolio
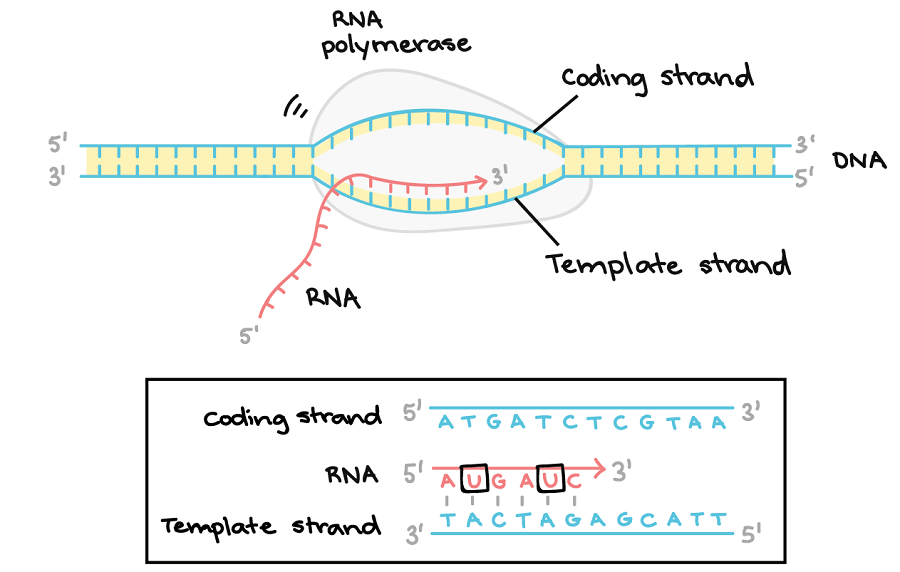
DNA Transcription (RNA Synthesis) Article, Diagrams and Video

DNA Strands PowerPoint Template SlideModel

Difference Between Template and Coding Strand Definition

Template And Coding Strand

Dna Template Sequence
Web An Mrna Transcript Is A Single Strand Of Rna That Encapsulate The Information Contained In A Gene.
This Video Explain The Difference Between A.
Web Transcription Always Proceeds From One Of The Two Dna Strands, Which Is Called The Template Strand.
Replication Relies On Complementary Base Pairing, That Is The Principle Explained By Chargaff's Rules:
Related Post: