Non Template Dna Strand
Non Template Dna Strand - The coding strand also runs from 5’ to 3’ direction. The bases are the same, except. Web transcription uses one of the two exposed dna strands as a template; This strand is called the template strand.the rna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate (or coding) strand.however, there is one important difference: Web by convention, the coding strand is the strand used when displaying a dna sequence. This work advances our understanding of transcription regulation and. The coding strand serves as a template for producing complementary rna. Wherever a gene exists on a dna molecule, one strand is the coding strand (or sense strand ), and the other is the noncoding strand (also called the antisense strand, [3] anticoding strand, template strand or. Understand that within a single piece of dna, either strand can be used as the template for different genes, but the rna will still be produced from 5’ → 3’. The transfer of parental histones occurs through two distinct pathways: Hence, coding strand is incapable of serving as the. In the newly made rna, all of the t. This is the strand that is used by convention when presenting a. Mrna bases are complementary to and bind to dna bases; Understand that within a single piece of dna, either strand can be used as the template for different genes, but. In the newly made rna, all of the t. Leading strand deposition, mediated by the dna polymerase ε subunits dpb3/dpb4, and lagging strand. It is presented in the 5' to 3' direction. Dna has a double helix structure meaning, it consists of two long polynucleotide chains that are. With the genes bound in the nucleus, transcription occurs in the nucleus. Transcription is elongated in the 5’ to 3’ direction by adding complementary nucleotides to the mrna strand. Transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand. The coding strand serves as a template for producing complementary rna. Web dna lock promotes elongation in the absence of rfah. In the newly made rna, all. This is the strand that is used by convention when presenting a. Web as it reads this template one base at a time, the polymerase builds an rna molecule out of complementary nucleotides, making a chain that grows from 5' to 3'. Web dsrna generation mechanisms during ivt. The coding strand serves as a template for producing complementary rna. The. Transcription is elongated in the 5’ to 3’ direction by adding complementary nucleotides to the mrna strand. This strand is called the template strand.the rna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate (or coding) strand.however, there is one important difference: Mrna bases are complementary to and bind to. Understand that within a single piece of dna, either strand can be used as the template for different genes, but the rna will still be produced from 5’ → 3’. The term template strand refers to the dna sequence that can duplicate itself during mrna synthesis. Your article has been reviewed by three peer reviewers, and the evaluation has been. Web coding strand vs. The transfer of parental histones occurs through two distinct pathways: Your article has been reviewed by three peer reviewers, and the evaluation has been overseen by a reviewing editor and gisela storz as the senior editor. Dna has a double helix structure meaning, it consists of two long polynucleotide chains that are. Leading strand deposition, mediated. The coding strand serves as a template for producing complementary rna. It is presented in the 5' to 3' direction. Your article has been reviewed by three peer reviewers, and the evaluation has been overseen by a reviewing editor and gisela storz as the senior editor. The coding strand also runs from 5’ to 3’ direction. Web as it reads. Dna has a double helix structure meaning, it consists of two long polynucleotide chains that are. It is presented in the 5' to 3' direction. Web by convention, the coding strand is the strand used when displaying a dna sequence. Wherever a gene exists on a dna molecule, one strand is the coding strand (or sense strand ), and the. Web transcription uses one of the two exposed dna strands as a template; This strand is called the template strand.the rna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate (or coding) strand.however, there is one important difference: The coding strand serves as a template for producing complementary rna. Transcription. In the newly made rna, all of the t. Wherever a gene exists on a dna molecule, one strand is the coding strand (or sense strand ), and the other is the noncoding strand (also called the antisense strand, [3] anticoding strand, template strand or. The transfer of parental histones occurs through two distinct pathways: This is the strand that is used by convention when presenting a. Leading strand deposition, mediated by the dna polymerase ε subunits dpb3/dpb4, and lagging strand. Mrna bases are complementary to and bind to dna bases; Hence, coding strand is incapable of serving as the. Web dna lock promotes elongation in the absence of rfah. Web by convention, the coding strand is the strand used when displaying a dna sequence. Transcription is elongated in the 5’ to 3’ direction by adding complementary nucleotides to the mrna strand. The genetic instructions for various cellular processes of living organisms are carried in the dna molecule. With the genes bound in the nucleus, transcription occurs in the nucleus of the cell and the mrna transcript must be. Web transcription uses one of the two exposed dna strands as a template; It is presented in the 5' to 3' direction. Transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand. Your article has been reviewed by three peer reviewers, and the evaluation has been overseen by a reviewing editor and gisela storz as the senior editor.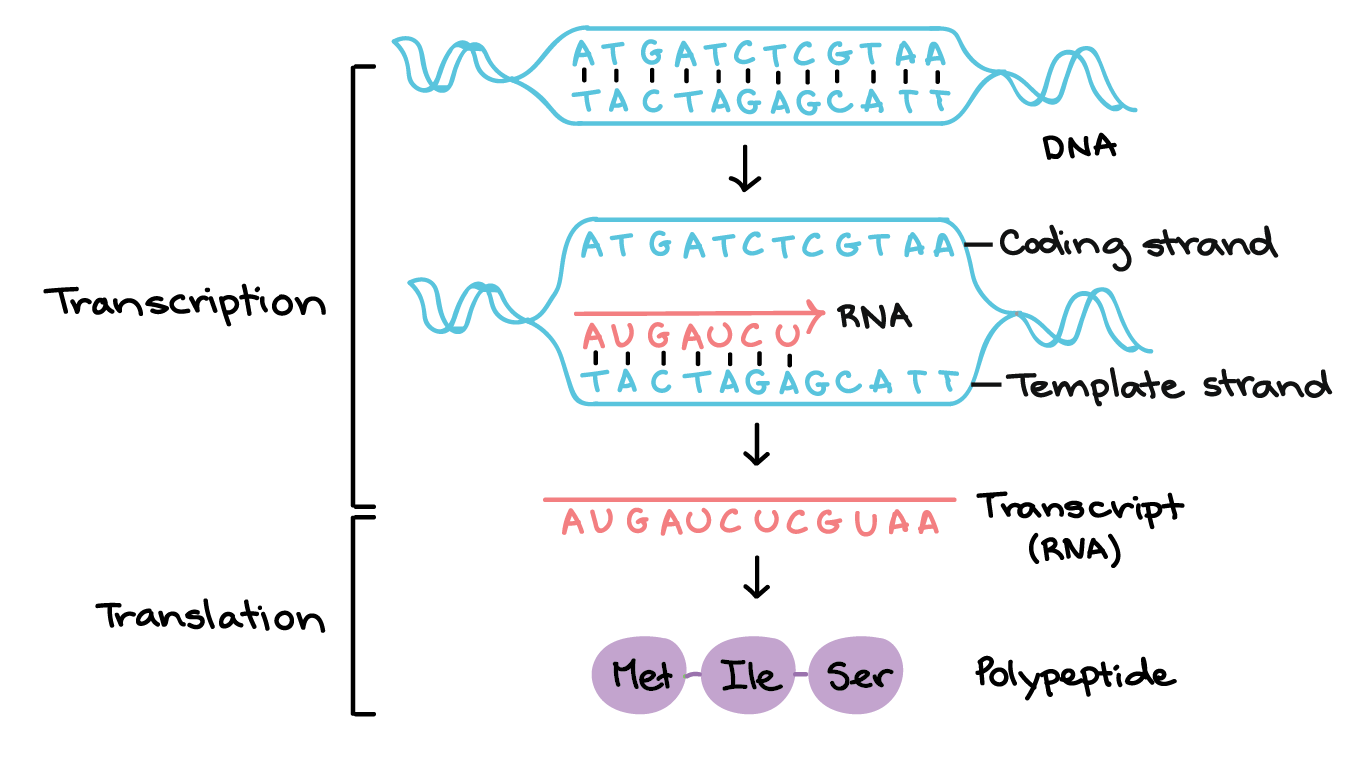
What strand of DNA is used to make a complementary copy or to make a
RNA Transcription Fundamentals and Key Terms on the MCAT MCAT Mastery

Non Template Strand

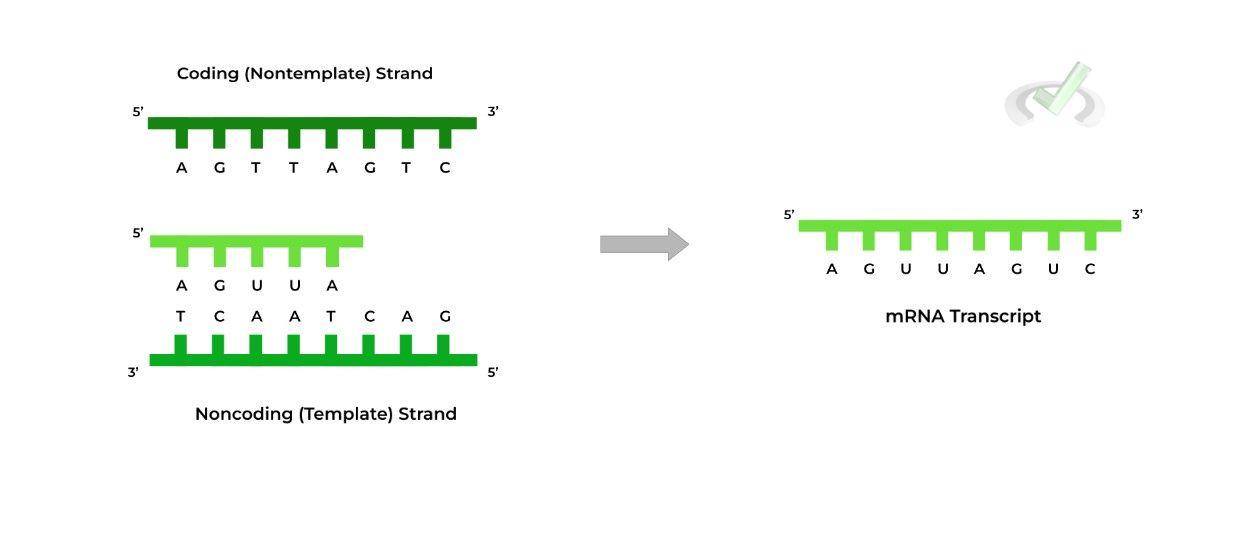
Template DNA base pairing with the nontemplate DNA base at the10th

Chapter The Code — The Biology Primer

Non Template Dna Strand

Participation of the nontemplate DNA strand in HQ formation detected

Solved Part A (3 points) Nontemplate strand of DNA Template

Coding NonCoding Sense Antisense Template and NonTemplate Strands
Non Template Strand
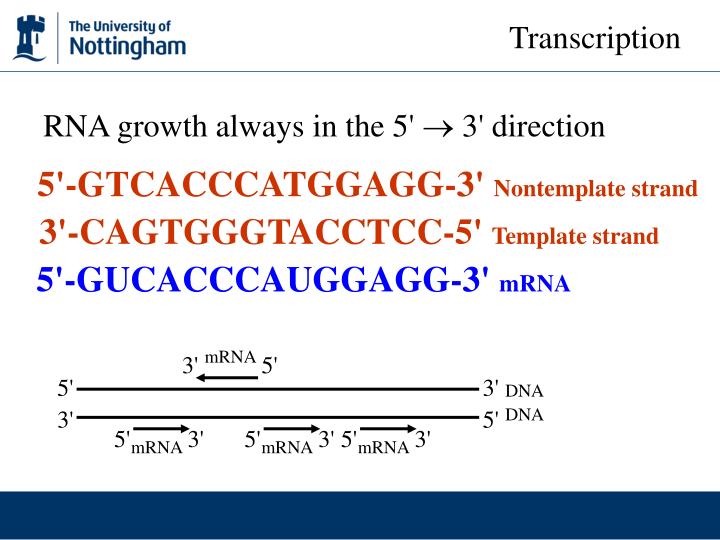
Web Once Transcription Is Initiated, The Dna Double Helix Unwinds And Rna Polymerase Reads The Template Strand, Adding Nucleotides To The 3′ End Of The Growing Chain (Figure 2B).
The Bases Are The Same, Except.
Web Rfah Is Recruited At Ops Sites In Vitro And In Vivo (Artsimovitch And Landick, 2002;
The Mrna Product Is Complementary To The Template Strand And Is Almost Identical To The Other Dna Strand, Called The Nontemplate Strand, With The Exception That Rna Contains A Uracil (U) In Place Of The Thymine (T) Found In Dna.
Related Post: