Template Dna Definition
Template Dna Definition - Web polymerases are classified according to the type of template that they use. An investigator is studying the transcription of dna in a mouse model. Each new double strand consists of one parental strand and one new daughter strand. Sequencing an entire genome (all of an organism’s dna) remains a complex task. This is the stand of dna the taq polymerase is going to use for amplification. Web a segment of dna that codes for the cell’s synthesis of a specific protein is called a gene. The nontemplate strand is referred. Initiation of protein synthesis p. These enzymes utilize energy from atp to move on dna, destabilize the hydrogen bonds between bases, and separate the two strands of the double helix. Dna templates linked to a capture bead are exposed to only one dntp during each round of sequencing. Web 6 mins read. Web polymerases are classified according to the type of template that they use. It is the strand of dna that does not directly code for a protein but complementarily pairs with the code so it can. Memory anchors and partner content. Initiation of protein synthesis p. The new strand will be complementary to the parental or “old” strand. During dna replication, the template is generated by enzymes known as helicases. This is the stand of dna the taq polymerase is going to use for amplification. Deoxyribonucleic acid, or dna, is a biological macromolecule that carries hereditary information in many organisms. Each strand in the double helix. An investigator is studying the transcription of dna in a mouse model. To preserve biological information, it is essential that the sequence of bases in each copy are precisely complementary to the sequence of bases in the template strand. Memory anchors and partner content. Dna replicates by separating into two single strands, each of which serves as a template for. These enzymes utilize energy from atp to move on dna, destabilize the hydrogen bonds between bases, and separate the two strands of the double helix. The primary enzyme involved in this is dna polymerase which joins nucleotides to synthesize the. The new strand will be complementary to the parental or “old” strand. In eukaryotes, the rna must go through additional. The sequence of a, t, g, c nucleotides in a dna template and a, u, g, c nucleotides in an rna template codes for information that can be transferred through complementary watson. Either dna strand can be a template. Each new double strand consists of one parental strand and one new daughter strand. Initiation of protein synthesis p. Web during. Web dna sequencing is the process of determining the sequence of nucleotide bases (as, ts, cs, and gs) in a piece of dna. Web a technique used to amplify, or make many copies of, a specific target region of dna. This is the stand of dna the taq polymerase is going to use for amplification. Polymerase chain reaction, or pcr,. Dna replicates by separating into two single strands, each of which serves as a template for a new strand. An investigator is studying the transcription of dna in a mouse model. This is known as semiconservative. Polymerase chain reaction, or pcr, is a technique to make many copies of a specific dna region in vitro (in a test tube rather. Web a segment of dna that codes for the cell’s synthesis of a specific protein is called a gene. An investigator is studying the transcription of dna in a mouse model. Web so, what is the template strand of dna? Either dna strand can be a template. Dna is necessary for the production of proteins, the regulation, metabolism, and reproduction. The new strand will be complementary to the parental or “old” strand. Each strand in the double helix acts as a template for synthesis of a new, complementary strand. Dna is necessary for the production of proteins, the regulation, metabolism, and reproduction of the cell. Web each strand then serves as a template for a new complementary strand to be. During elongation, rna polymerase walks along one strand of dna, known as the template strand, in the 3' to 5' direction. Overview of the stages of transcription. What is dna template strand? In eukaryotes, the rna must go through additional processing steps to become a messenger rna, or mrna. Web dna sequencing is the process of determining the sequence of. Dna templates linked to a capture bead are exposed to only one dntp during each round of sequencing. During elongation, rna polymerase walks along one strand of dna, known as the template strand, in the 3' to 5' direction. Initiation of protein synthesis p. Web a technique used to amplify, or make many copies of, a specific target region of dna. Web 6 mins read. Major types of cellular rna. An investigator is studying the transcription of dna in a mouse model. Today, with the right equipment and materials, sequencing a short piece of dna is relatively straightforward. Either dna strand can be a template. New dna is made by enzymes called dna polymerases, which require a template and a primer (starter) and synthesize dna in the 5' to 3' direction. These enzymes utilize energy from atp to move on dna, destabilize the hydrogen bonds between bases, and separate the two strands of the double helix. The nontemplate strand is referred. Identify the key steps of transcription, the function of the promoter and the function of rna polymerase. The new strand will be complementary to the parental or “old” strand. The primary enzyme involved in this is dna polymerase which joins nucleotides to synthesize the. Overview of the stages of transcription.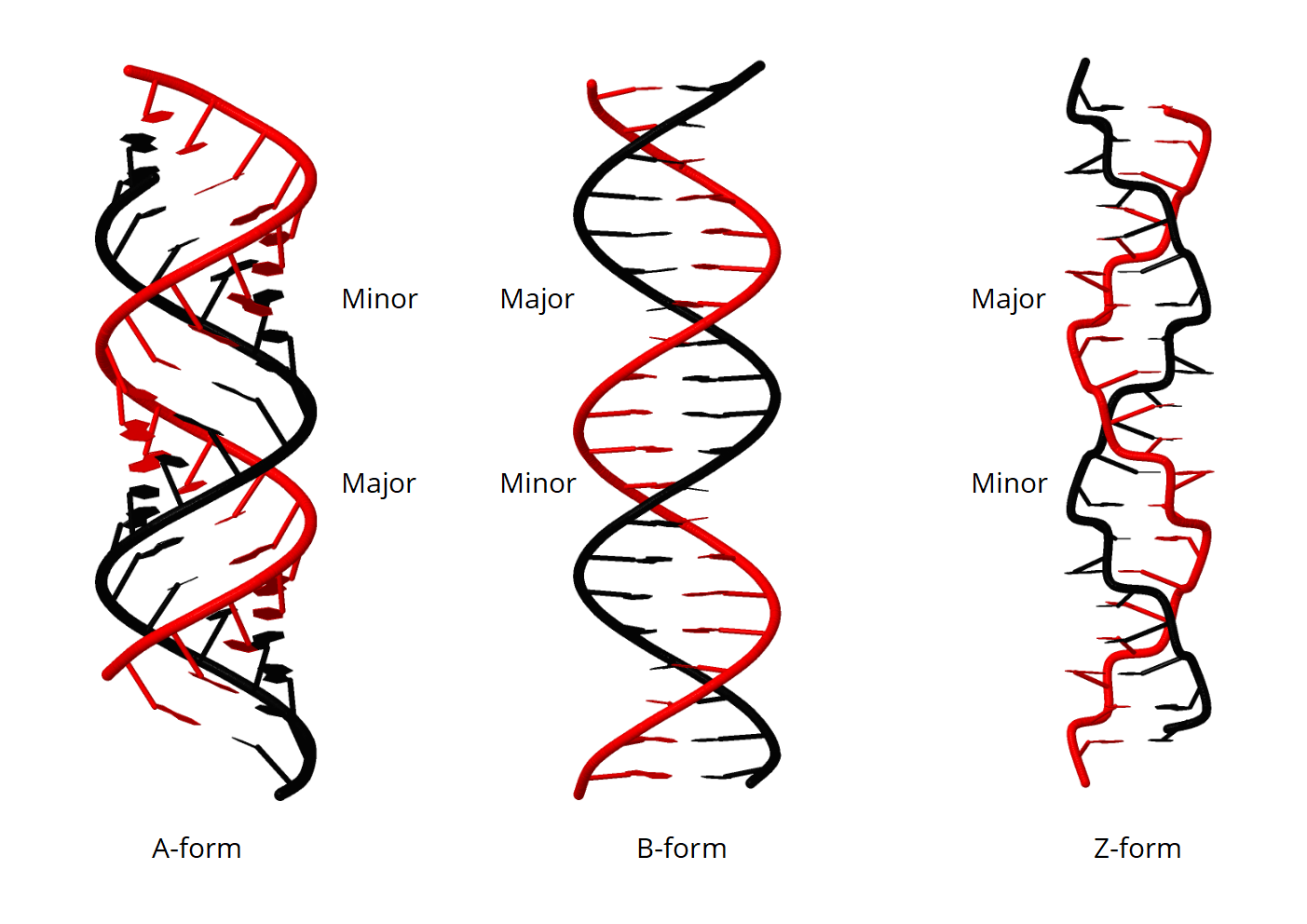
Dna Template Definition
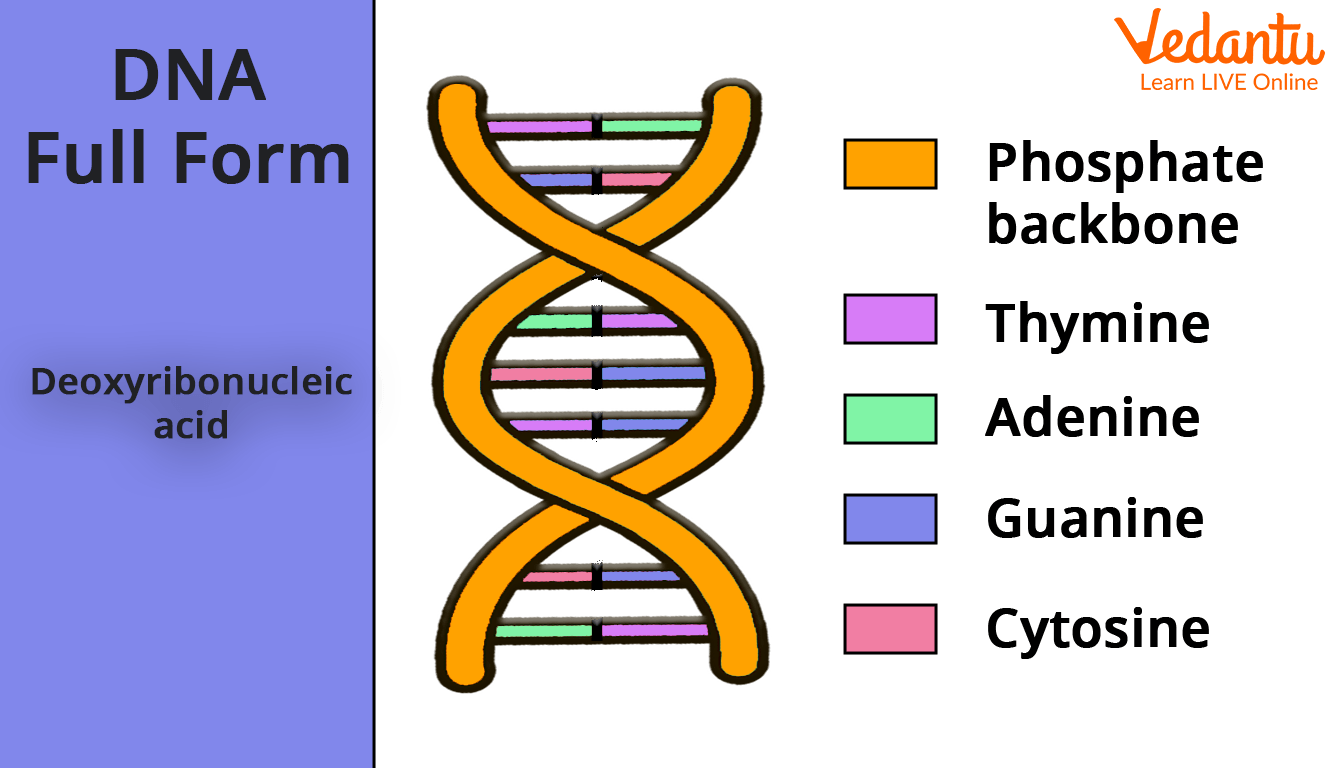
DNA for Kids Learn Definition, Structure, Functions & Facts
/3-D_DNA-56a09ae45f9b58eba4b20266.jpg)
DNA Definition Shape, Replication, and Mutation

DNA Definition, Function, Structure and Discovery Biology Dictionary
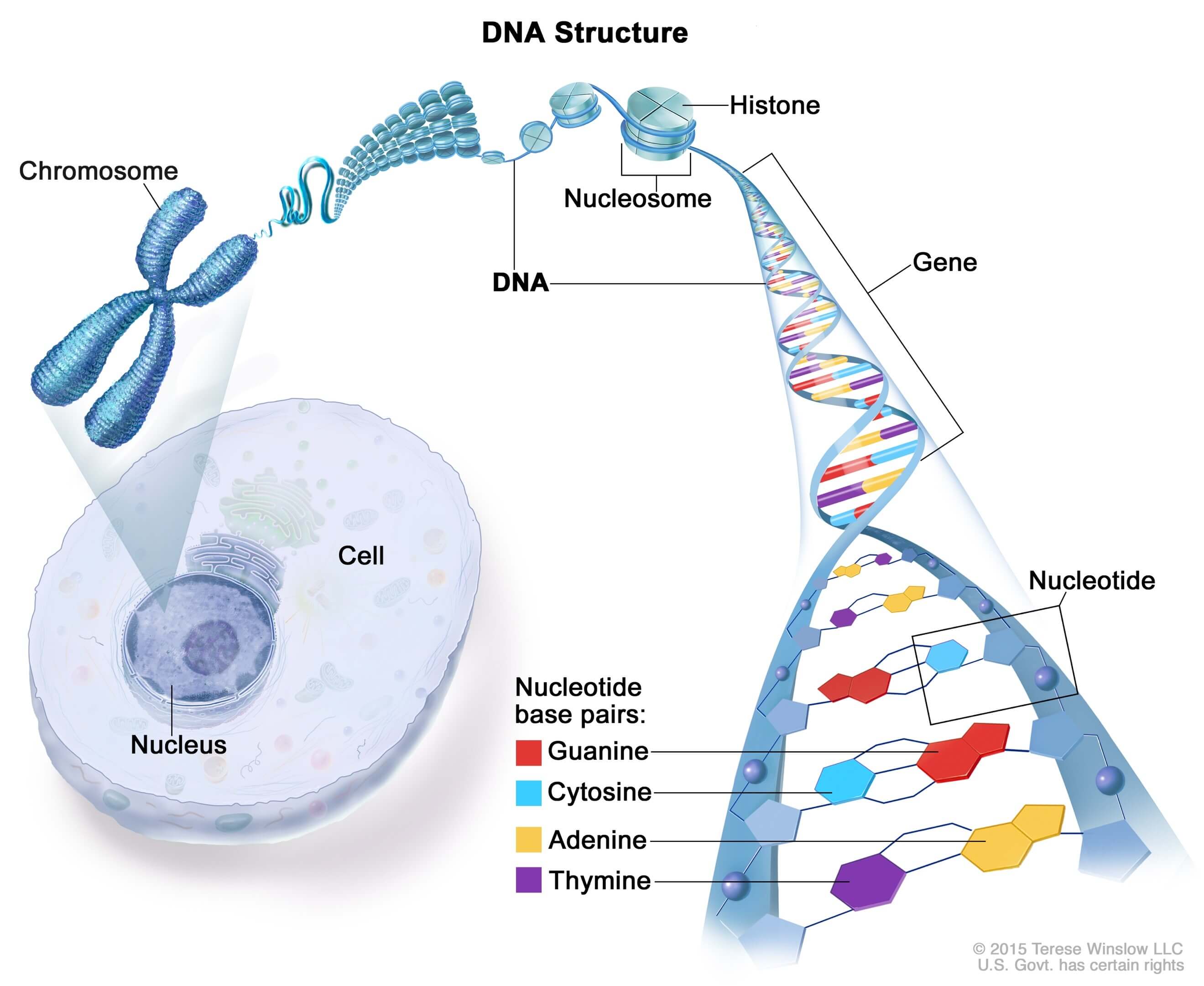
DNA Full Form Guide for Beginners to Understand What it Is

What is DNA Definition, Structure, Funtion & Discovery

DNA Structure & DNA Replication Biology Online Tutorial

The Nucleus and DNA Replication Anatomy and Physiology I

Replication Britannica
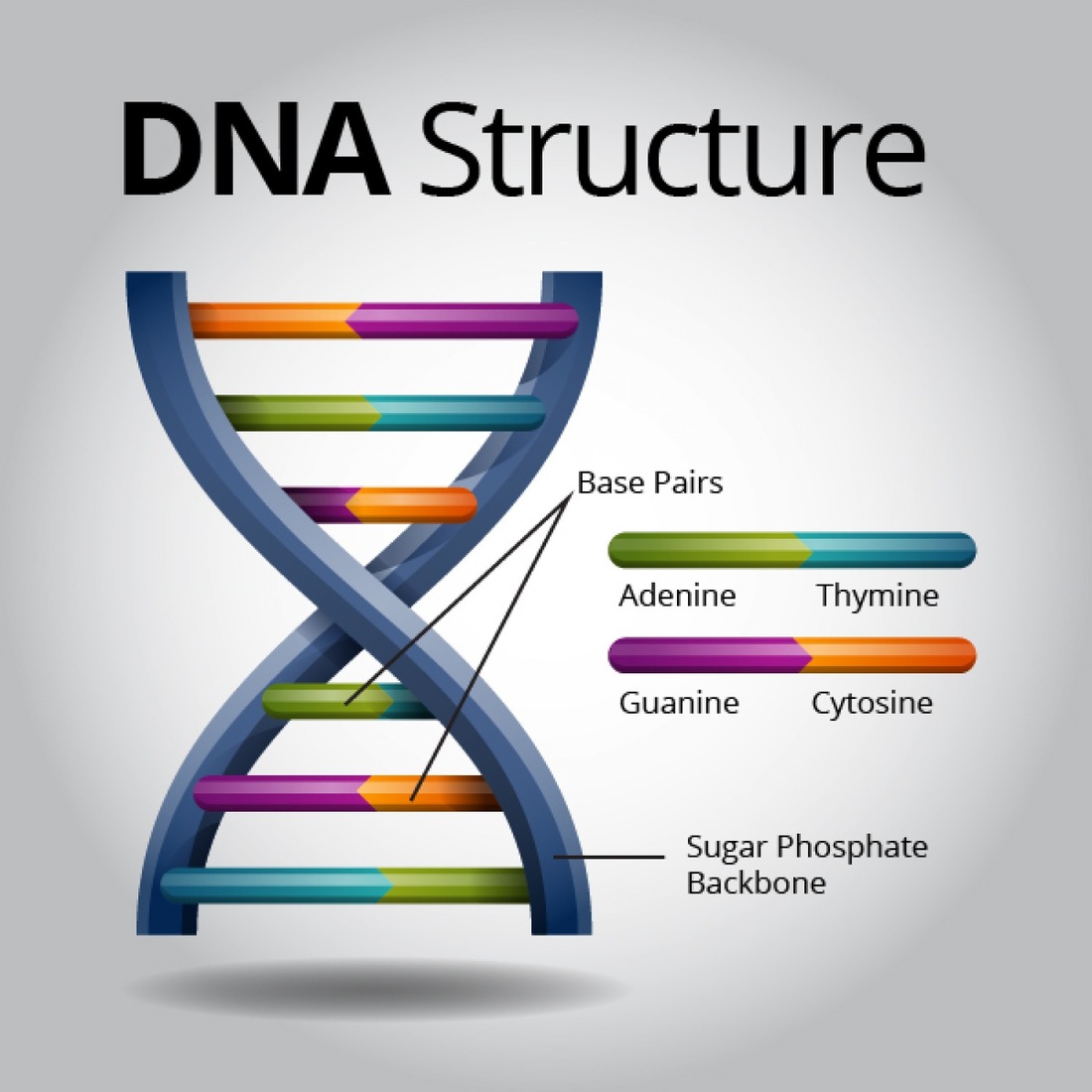
DNA AP Biology Portfolio
Web Basically, E Long Ation Is The Stage When The Rna Strand Gets Long Er, Thanks To The Addition Of New Nucleotides.
Web Dna Sequencing Is The Process Of Determining The Sequence Of Nucleotide Bases (As, Ts, Cs, And Gs) In A Piece Of Dna.
It Is The Strand Of Dna That Does Not Directly Code For A Protein But Complementarily Pairs With The Code So It Can.
Sequencing An Entire Genome (All Of An Organism’s Dna) Remains A Complex Task.
Related Post: