Template Dna Strand
Template Dna Strand - A short sequence of dna or rna that is complementary to the template strand will work to provide a free 3′ end. Web primer and template. Replication produces two identical dna double helices, each with one new and one old strand. The addition of nucleotides occurs in the 5’ to 3’ direction. Some people think that in the leading strand, dna is synthesized in the 5’ to 3’ direction, while in lagging strand, dna is synthesized in the 3’ to 5. In the newly made rna, all of the t. The mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand , with the exception that rna contains a uracil (u) in place of the thymine (t) found in dna. Web the dna template is used by rna polymerase to produce a strand of rna with a nucleotide sequence that is the same as the coding strand for the production of functional rna units and mrna for. Web given a dna sequence alone, you can annotate open reading frames (orfs) in order to identify the coding strand, with the caveat that not all orfs are genes. Depending on the promoter, either strand of dna can be used as the template strand. Web either dna strand can be a template. Web given a dna sequence alone, you can annotate open reading frames (orfs) in order to identify the coding strand, with the caveat that not all orfs are genes. How does dna polymerase know in what order to add nucleotides? It involves copying a gene's dna sequence to make an rna molecule.. Some people think that in the leading strand, dna is synthesized in the 5’ to 3’ direction, while in lagging strand, dna is synthesized in the 3’ to 5. Web given a dna sequence alone, you can annotate open reading frames (orfs) in order to identify the coding strand, with the caveat that not all orfs are genes. Web actually,. Web the template strand, on the other hand, has a sequence of nucleotides that is complementary to the sequence on the coding strand. Specific base pairing in dna is. In the newly made rna, all of the t. Dna polymerase uses a single strand of dna as a template and synthesizes a strand of dna. This way, both strands work. Transcription is performed by enzymes called rna polymerases, which link nucleotides to form an rna strand (using a dna strand as a. Transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand.the mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with. Rna polymerase adds complementary nucleotides to the nucleotides that are encoded in the template strand in order to form the primary rna transcript. In the newly made rna, all of the t. This process takes us from one starting molecule to two daughter molecules, with each newly formed double helix containing one new and one old strand. A bit like. Web dna replication is semiconservative, meaning that each strand in the dna double helix acts as a template for the synthesis of a new, complementary strand. Web the template strand, on the other hand, has a sequence of nucleotides that is complementary to the sequence on the coding strand. Web a dna template strand generally refers to the strand which. Web given a dna sequence alone, you can annotate open reading frames (orfs) in order to identify the coding strand, with the caveat that not all orfs are genes. Specific base pairing in dna is. In such cases, wither the molecule moves down towards the strand in the direction of 3’. Web chromatin replication is intricately intertwined with the recycling. This way, both strands work together, ensuring the right information is transferred from dna to rna. Dna polymerase needs an “anchor” to start adding nucleotides: How does dna polymerase know in what order to add nucleotides? The arrow is labeled primer 2 and there are 12 bases paired with the dna template strand with as paired with ts and cs. Web transcription uses one of the two exposed dna strands as a template; The coding strand is the other strand of dna helix other than the template strand that runs from 5' to 3' end and is parallel to the mrna strand. Some people think that in the leading strand, dna is synthesized in the 5’ to 3’ direction, while. The addition of nucleotides occurs in the 5’ to 3’ direction. Web transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand. Web transcription uses one of the two exposed dna strands as a template; The promoter is the sequence of dna that encodes the information about where to begin transcription for each gene.. Web dna replication is semiconservative, meaning that each strand in the dna double helix acts as a template for the synthesis of a new, complementary strand. The promoter is the sequence of dna that encodes the information about where to begin transcription for each gene. In such cases, wither the molecule moves down towards the strand in the direction of 3’. Web primer and template. Web actually, the mrna strand is coded from the template strand of the dna which runs from 3' to 5' end. Transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand.the mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with the exception that rna contains a uracil (u) in place of the thymine (t) found in dna.during. Comment button navigates to signup page (2 votes) The transfer of parental histones occurs through two distinct pathways: Rna polymerase adds complementary nucleotides to the nucleotides that are encoded in the template strand in order to form the primary rna transcript. Web a dna template strand generally refers to the strand which is used by the enzyme dna polymerases and rna polymerases to attach with the complementary bases during the process of replication of dna or at the time of transcription of rna respectively. How does dna polymerase know in what order to add nucleotides? A short sequence of dna or rna that is complementary to the template strand will work to provide a free 3′ end. Web transcription uses one of the two exposed dna strands as a template; This is because its base sequence is identical to the synthesised mrna, except for the replacement of thiamine bases with. Web chromatin replication is intricately intertwined with the recycling of parental histones to the newly duplicated dna strands for faithful genetic and epigenetic inheritance. Leading strand deposition, mediated by the dna polymerase ε subunits dpb3/dpb4, and lagging strand.
DNA Strands Template Download & Edit PowerSlides™

DNA Strands PowerPoint Template SlideModel

Replication Britannica
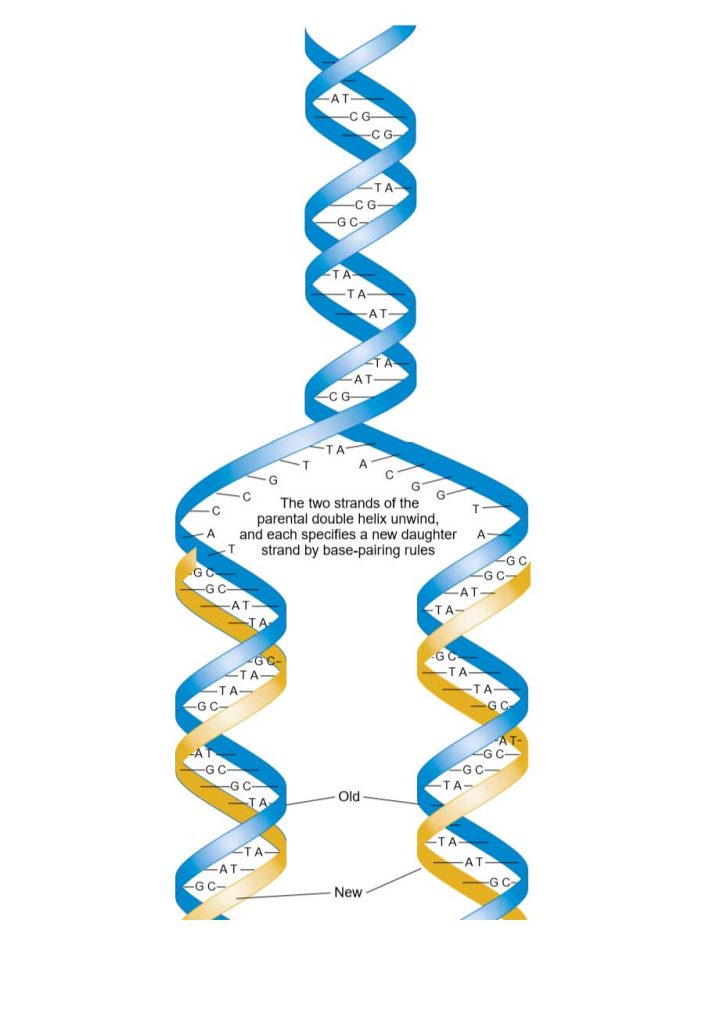
Dna Serves As A Template For The Synthesis Of

DNA Replication Stages of Replication TeachMePhyiology

Chapter The Code — The Biology Primer

Coding Strand vs. Template Strand 6 Key Variations sciencesavers
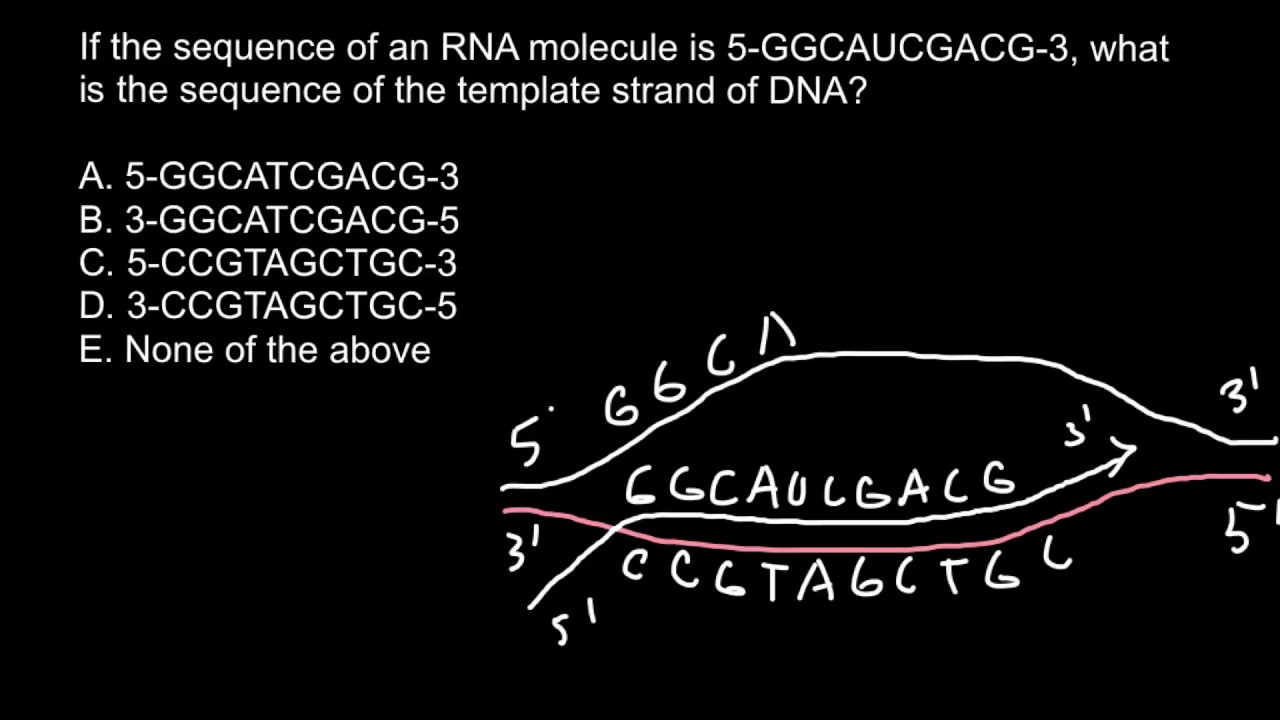
How to find sequence of the template strand of DNA YouTube
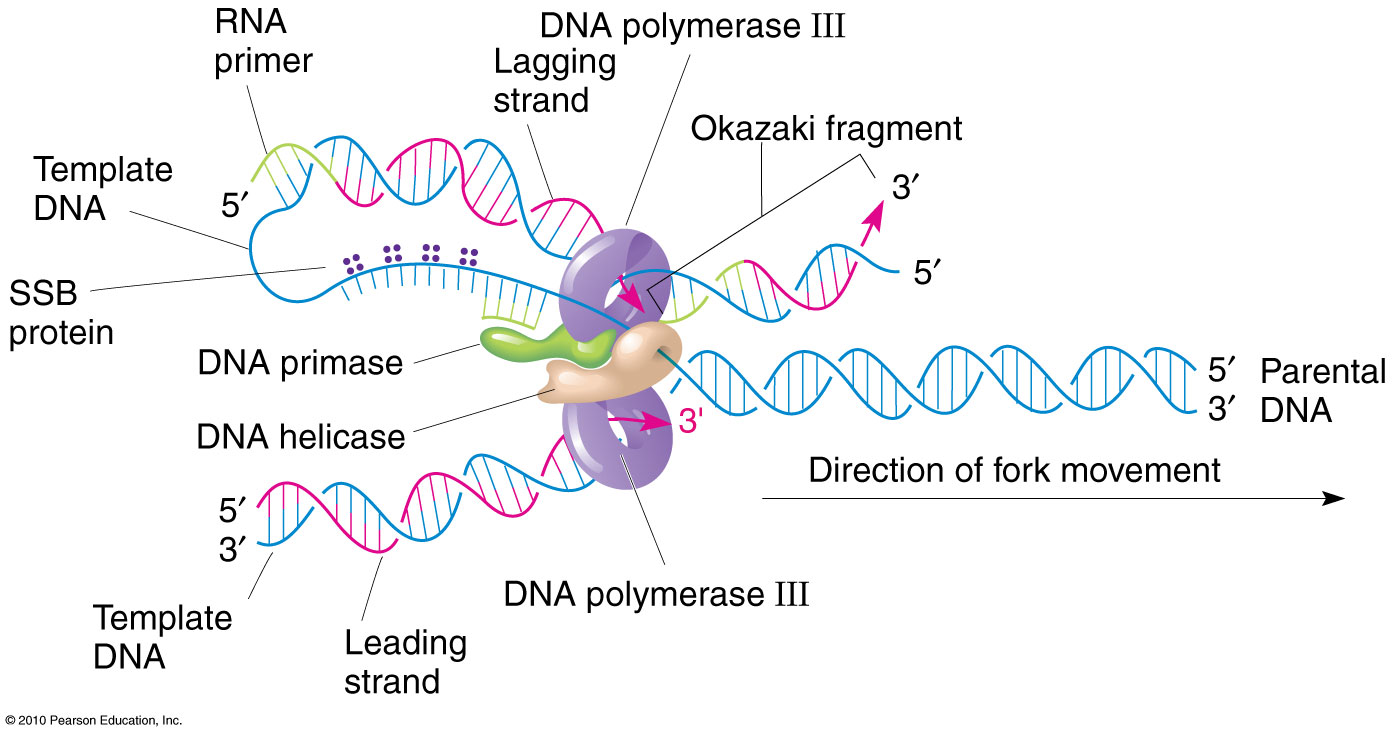
What Is The Template Strand Of Dna
DNA Strands PowerPoint Template SlideModel
Some People Think That In The Leading Strand, Dna Is Synthesized In The 5’ To 3’ Direction, While In Lagging Strand, Dna Is Synthesized In The 3’ To 5.
Specific Base Pairing In Dna Is.
This Process Takes Us From One Starting Molecule To Two Daughter Molecules, With Each Newly Formed Double Helix Containing One New And One Old Strand.
The Other Dna Strand Is Referred To As The Coding Strand.
Related Post: