Template For Dna Replication
Template For Dna Replication - Web transcription and replication use the same genomic dna as a template. Semi conservative because once dna molecule is synthesized it has one strand from the parent and the other strand is a newly formed strand. Explain the meaning of semiconservative dna replication. Previously, it was thought that cells separate transcription and replication temporally and spatially. Web during dna replication, each of the two strands that make up the double helix serves as a template from which new strands are copied. Adenine (a) always bonds with thymine (t) and cytosine (c) always bonds with guanine (g). What makes death cap mushrooms deadly? Mrna, a scrupulous rna copy of the ‘coding’ strand of dna (also known as ‘sense’ or ‘plus’ strand), is translated into amino acid polymers (polypeptides) by the ribosomal machinery. The models were tested by meselson and stahl, who labeled the dna of bacteria across generations using isotopes of nitrogen. The new strand will be complementary to the parental or “old” strand. The new strand will be complementary to the parental or “old” strand. Hence, conflicts between these two machineries are inevitable. The strand of the template dna double helix that is oriented so that the replication fork moves along it in a 5′ to 3′ manner; Web in simple terms, replication involves use of an existing strand of dna as a. Web rna polymerase uses one of the dna strands (the template strand) as a template to make a new, complementary rna molecule. This template strand is called the noncoding strand. Web as a semiconservative process, a single molecule containing two strands of dna in double helix formation is separated, where each strand serves as a template for the new dna. The models were tested by meselson and stahl, who labeled the dna of bacteria across generations using isotopes of nitrogen. Explain why dna replication is bidirectional and includes both a leading and lagging strand. Adenine only pairs with thymine and cytosine only binds with guanine. In conservative replication, the parental dna is conserved, and the daughter dna is newly synthesized.. Transcription ends in a process called termination. Mrna, a scrupulous rna copy of the ‘coding’ strand of dna (also known as ‘sense’ or ‘plus’ strand), is translated into amino acid polymers (polypeptides) by the ribosomal machinery. The dna template is read in 3′ to 5′ direction whereas a new strand is synthesized in the 5′ to 3′ direction—this is often. Web as discussed in chapter 3, dna replication is a semiconservative process in which each parental strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary daughter strand. Web in a round of replication, each of the two strands of dna is used as a template for the formation of a complementary dna strand. Explain why okazaki fragments. Transcription ends in a process called termination. Explain why dna replication is bidirectional and includes both a leading and lagging strand. New dna is made by enzymes called dna polymerases, which require a template and a primer (starter) and synthesize dna in the 5' to 3' direction. Because eukaryotic genomes are quite complex, dna replication is a very complicated process. Web as a semiconservative process, a single molecule containing two strands of dna in double helix formation is separated, where each strand serves as a template for the new dna molecules. Web during dna replication, each of the two strands that make up the double helix serves as a template from which new strands are copied. Semi conservative because once. The models were tested by meselson and stahl, who labeled the dna of bacteria across generations using isotopes of nitrogen. Web rna is also used as a template for creating proteins. Replication occurs in three major steps: Mrna, a scrupulous rna copy of the ‘coding’ strand of dna (also known as ‘sense’ or ‘plus’ strand), is translated into amino acid. Web during dna replication, each of the two strands that make up the double helix serves as a template from which new strands are copied. Web rna polymerase uses one of the dna strands (the template strand) as a template to make a new, complementary rna molecule. The opening of the double helix and separation. Web as a semiconservative process,. Explain why dna replication is bidirectional and includes both a leading and lagging strand. The nontemplate strand is referred. Transcription ends in a process called termination. Mrna, a scrupulous rna copy of the ‘coding’ strand of dna (also known as ‘sense’ or ‘plus’ strand), is translated into amino acid polymers (polypeptides) by the ribosomal machinery. Web rna is also used. Because eukaryotic genomes are quite complex, dna replication is a very complicated process that involves several enzymes and other proteins. The new strand will be complementary to the parental or “old” strand. Dna has four bases called adenine (a), thymine (t), cytosine (c), and guanine (g) that form pairs between the two strands. The scope of the problem. New dna is made by enzymes called dna polymerases, which require a template and a primer (starter) and synthesize dna in the 5' to 3' direction. Web during dna replication, each of the two strands that make up the double helix serves as a template from which new strands are copied. The models were tested by meselson and stahl, who labeled the dna of bacteria across generations using isotopes of nitrogen. American enzymologist and nobel prize winner arthur kornberg. This template strand is called the noncoding strand. The opening of the double helix and separation. Web in a round of replication, each of the two strands of dna is used as a template for the formation of a complementary dna strand. Web the replication process relies on the fact that each strand of dna can serve as a template for duplication. Describe the process of dna replication and the functions of the enzymes involved. Web the model for dna replication suggests that the two strands of the double helix separate during replication, and each strand serves as a template from which the new complementary strand is copied. Adenine (a) always bonds with thymine (t) and cytosine (c) always bonds with guanine (g). Explain the meaning of semiconservative dna replication.
Steps of DNA Replication Infographic Template Visme
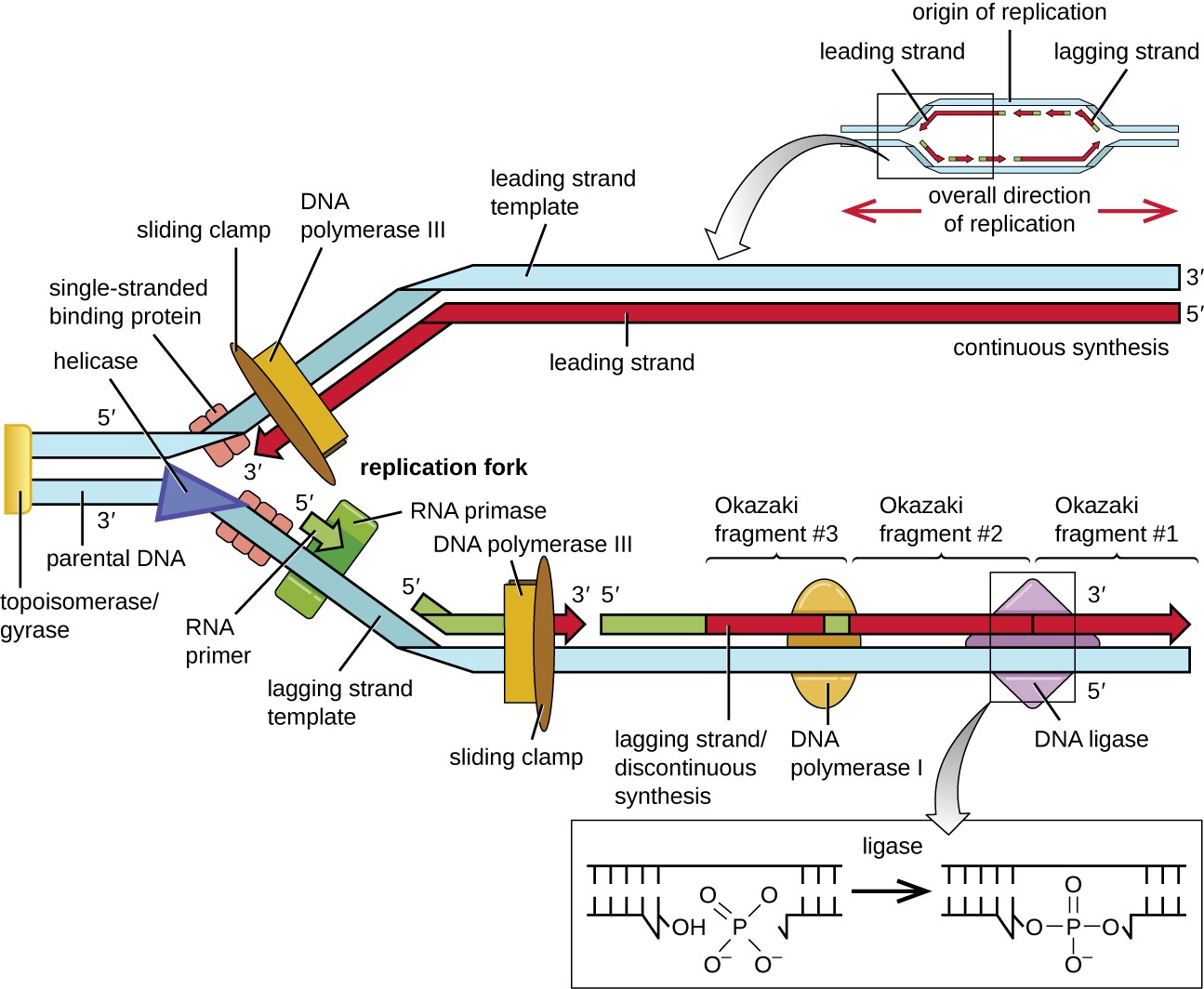
24.1 DNA Replication Biology LibreTexts

DNA Replication Stages of Replication TeachMePhyiology
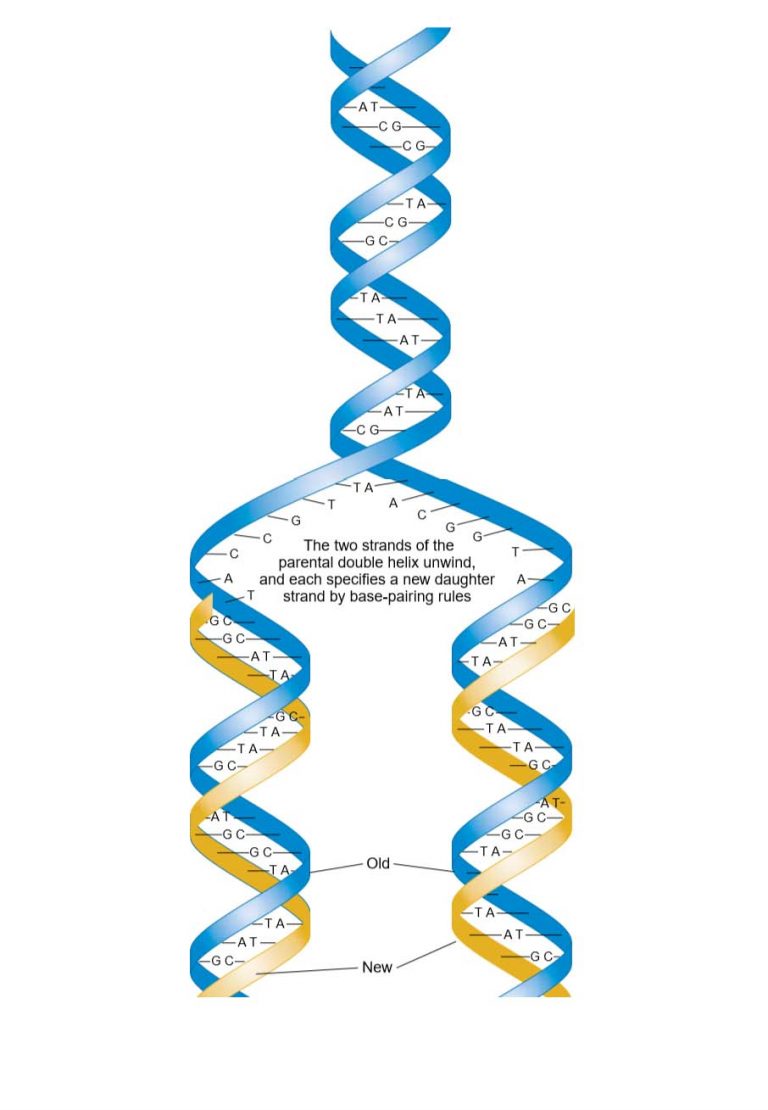
DNA Replication Study Solutions

What Acts As The Template In Dna Replication

This image shows the process of DNA replication. A chromosome is shown

DNA Structure & DNA Replication Biology Online Tutorial
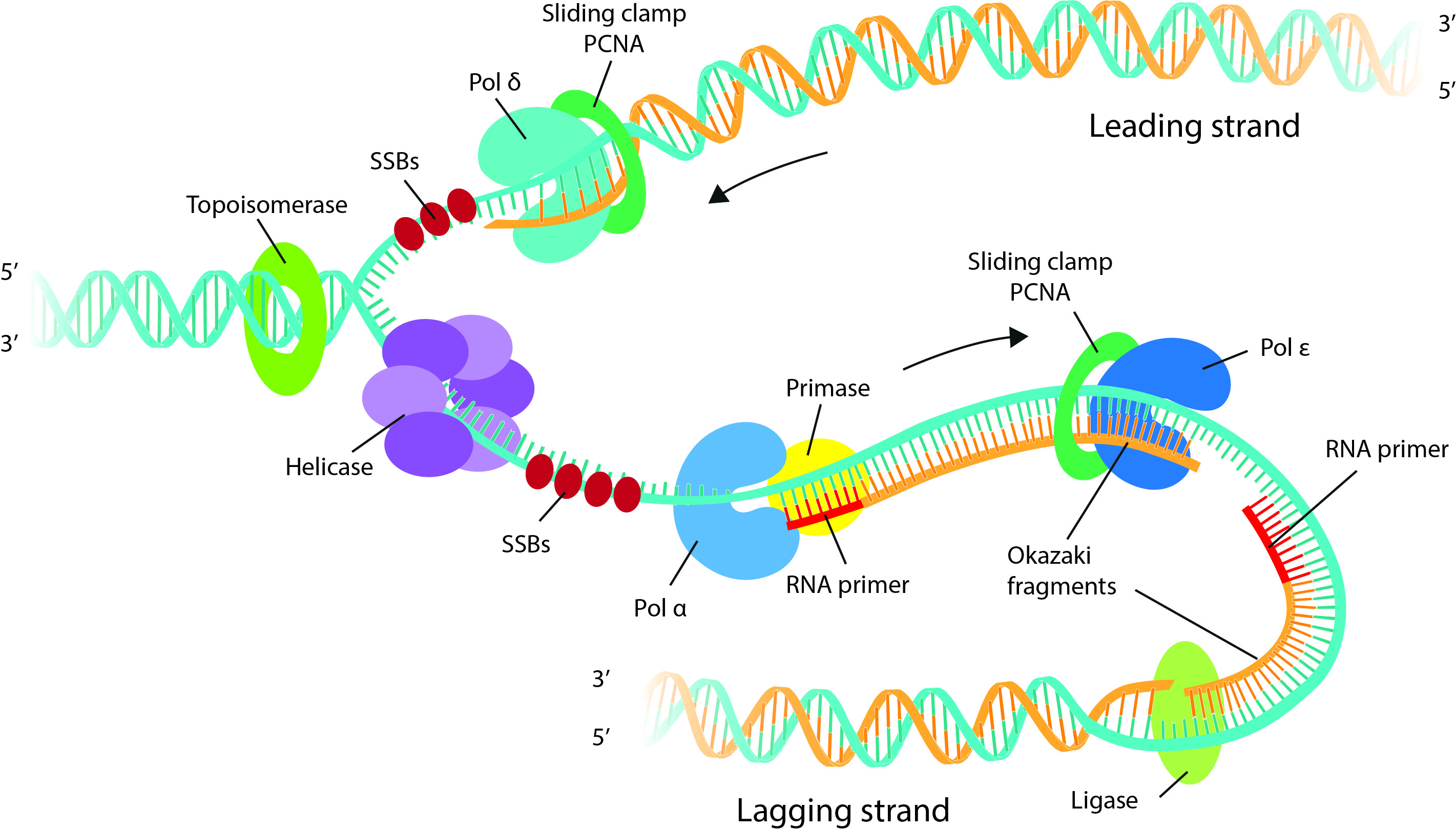
DNA Replication Lagging Strand

DNA Replication
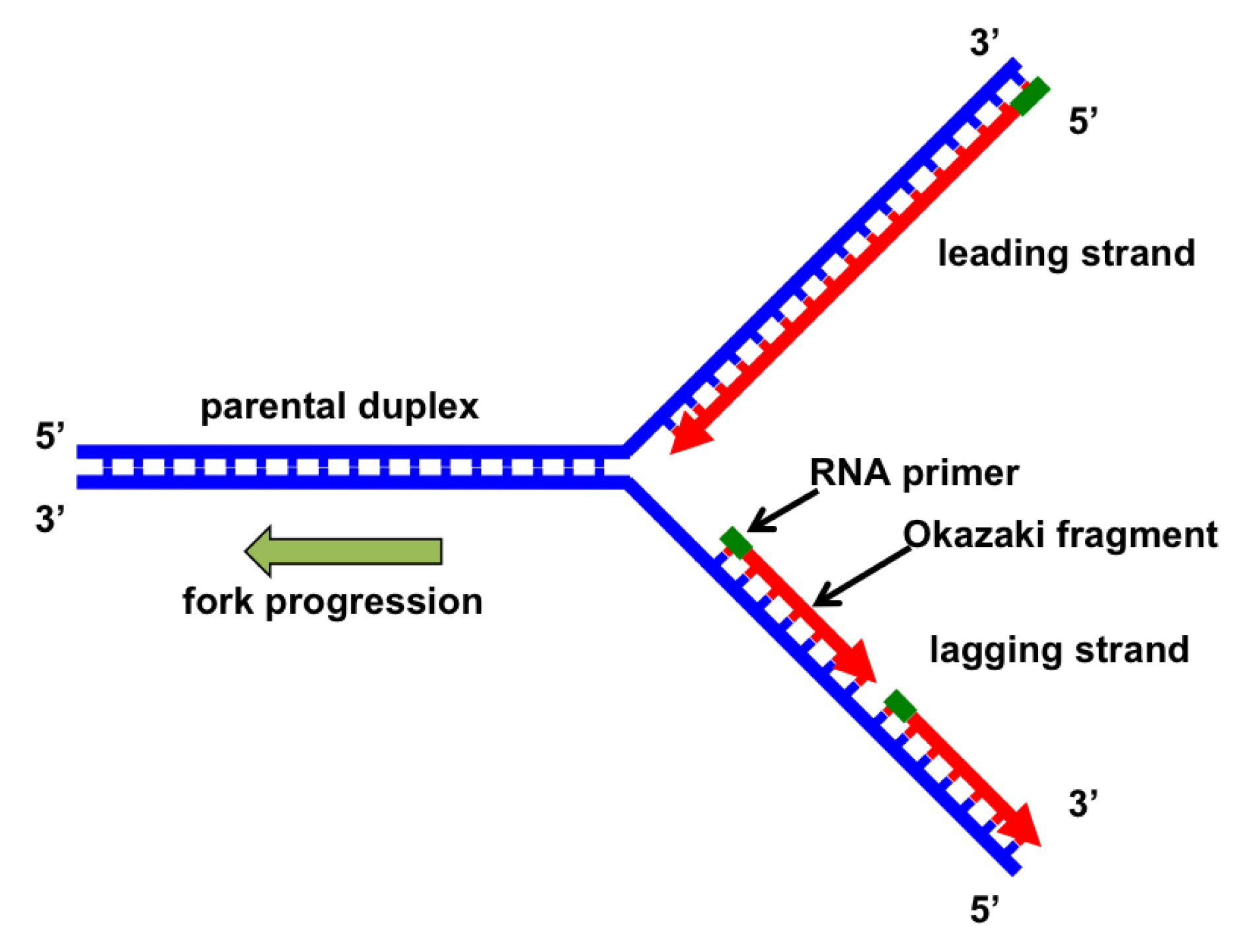
Genes Free FullText The Replication Fork Understanding the
Semi Conservative Because Once Dna Molecule Is Synthesized It Has One Strand From The Parent And The Other Strand Is A Newly Formed Strand.
In Conservative Replication, The Parental Dna Is Conserved, And The Daughter Dna Is Newly Synthesized.
Transcription Ends In A Process Called Termination.
Explain Why Dna Replication Is Bidirectional And Includes Both A Leading And Lagging Strand.
Related Post: