Template Strand In Dna
Template Strand In Dna - Web actually, the mrna strand is coded from the template strand of the dna which runs from 3' to 5' end. Web by convention, the coding strand is the strand used when displaying a dna sequence. Web in conservative replication, the parental dna is conserved, and the daughter dna is newly synthesized. Watch this video to see how either strand of dna can be used as a template for different genes on the. Transcription is performed by enzymes called rna polymerases, which link nucleotides to form an rna strand (using a dna strand as a. When transcription is completed, the rna is released, and the dna helix reforms. The other dna strand is referred to as the coding strand. It is presented in the 5' to 3' direction. In the newly made rna, all of the t. Transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand.the mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with the exception that rna contains a uracil (u) in place of the thymine (t) found in dna.during. In such cases, wither the molecule moves down towards the strand in the direction of 3’. Watch this video to see how either strand of dna can be used as a template for different genes on the. Web the dna double helix then unwinds, and rna synthesis begins at the start point on the template strand of dna. During elongation,. Web the diagram shows a template dna strand paired up with a new dna strand that is currently being synthesized. The addition of nucleotides occurs in the 5’ to 3’ direction. Dna replication occurs through the help of several enzymes. This strand is called the template strand.the rna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to. Web the dna double helix then unwinds, and rna synthesis begins at the start point on the template strand of dna. Web coding strand vs. Web transcription uses one of the two exposed dna strands as a template; These enzymes unzip dna molecules by breaking the hydrogen bonds that hold the two strands together. During elongation, the new rna strand. The addition of nucleotides occurs in the 5’ to 3’ direction. Web transcription uses one of the two exposed dna strands as a template; The promoter is the sequence of dna that encodes the information about where to begin transcription for each gene. Wherever a gene exists on a dna molecule, one strand is the coding strand (or sense strand. Web by convention, the coding strand is the strand used when displaying a dna sequence. Web synthesis of the rna strand takes place in the 5′ to 3′ direction, antiparallel to the template strand. The bases of the new strand and the template form complementary pairs held together by hydrogen bonds. In this view, the 5' end of the rna. Transcription is performed by enzymes called rna polymerases, which link nucleotides to form an rna strand (using a dna strand as a. Dna replication occurs through the help of several enzymes. Web transcription is the first step in gene expression. These enzymes unzip dna molecules by breaking the hydrogen bonds that hold the two strands together. Web either dna strand. It is presented in the 5' to 3' direction. Transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand. Web either dna strand can be a template. Web each strand of dna acts as a template for synthesis of a new, complementary strand. The complementary rna is created in the opposite direction, in the. Web by convention, the coding strand is the strand used when displaying a dna sequence. The interaction of pol32 with. Watch this video to see how either strand of dna can be used as a template for different genes on the. Transcription always proceeds from one of the two dna strands, which is called the template strand. The promoter is. The addition of nucleotides occurs in the 5’ to 3’ direction. The mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with the exception that rna contains a uracil (u) in place of the thymine (t) found in dna. During transcription, the enzyme rna polymerase (green) uses dna. This strand is called the template strand.the rna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate (or coding) strand.however, there is one important difference: Around them were bloodstains and their rifles. Rna polymerase adds complementary nucleotides to the nucleotides that are encoded in the template strand in order to. Dna is the hereditary material, passing traits from parents to offspring. Web the dna double helix then unwinds, and rna synthesis begins at the start point on the template strand of dna. Web each strand of dna acts as a template for synthesis of a new, complementary strand. The complementary rna is created in the opposite direction, in the 5' → 3' direction, matching the sequence of the sense strand except switching uracil. This strand is called the template strand.the rna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate (or coding) strand.however, there is one important difference: Web dna can now 'paint' such realistic images we can hardly tell. In the newly made rna, all of the t. The bases of the new strand and the template form complementary pairs held together by hydrogen bonds. Web synthesis of the rna strand takes place in the 5′ to 3′ direction, antiparallel to the template strand. The soldiers’ relatives identified their bodies from. Web by convention, the coding strand is the strand used when displaying a dna sequence. The genetic instructions for various cellular processes of living organisms are carried in the dna molecule. This is because its base sequence is identical to the synthesised mrna, except for the replacement of thiamine bases with. The other dna strand is referred to as the coding strand. Rna polymerase adds complementary nucleotides to the nucleotides that are encoded in the template strand in order to form the primary rna transcript. Watch this video to see how either strand of dna can be used as a template for different genes on the.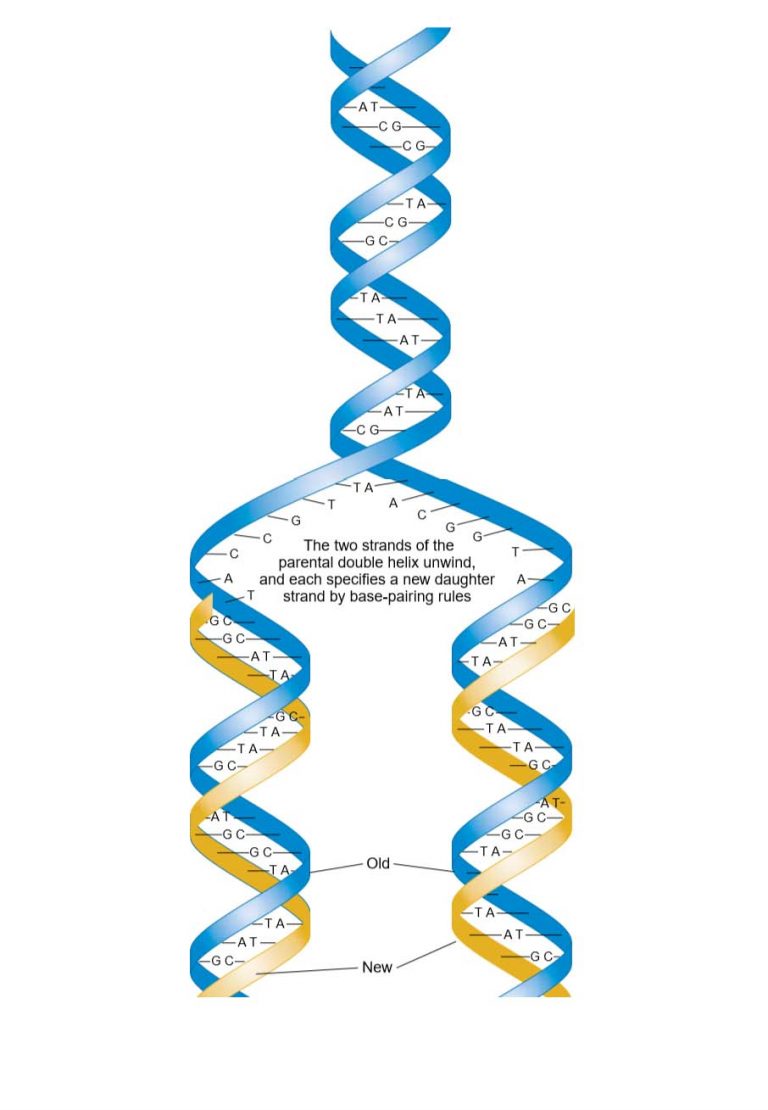
DNA Replication Study Solutions
DNA Strands PowerPoint Template SlideModel

Template Strand Of Dna
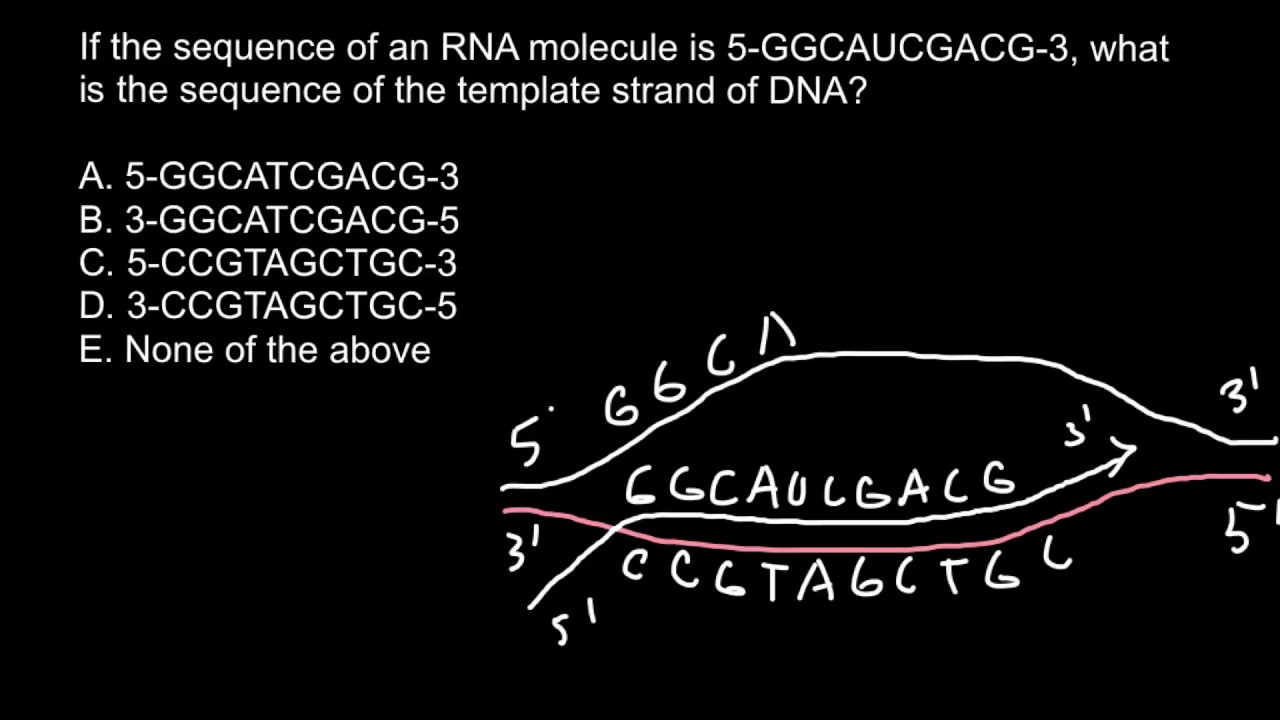
How to find sequence of the template strand of DNA YouTube

DNA Structure & DNA Replication Biology Online Tutorial
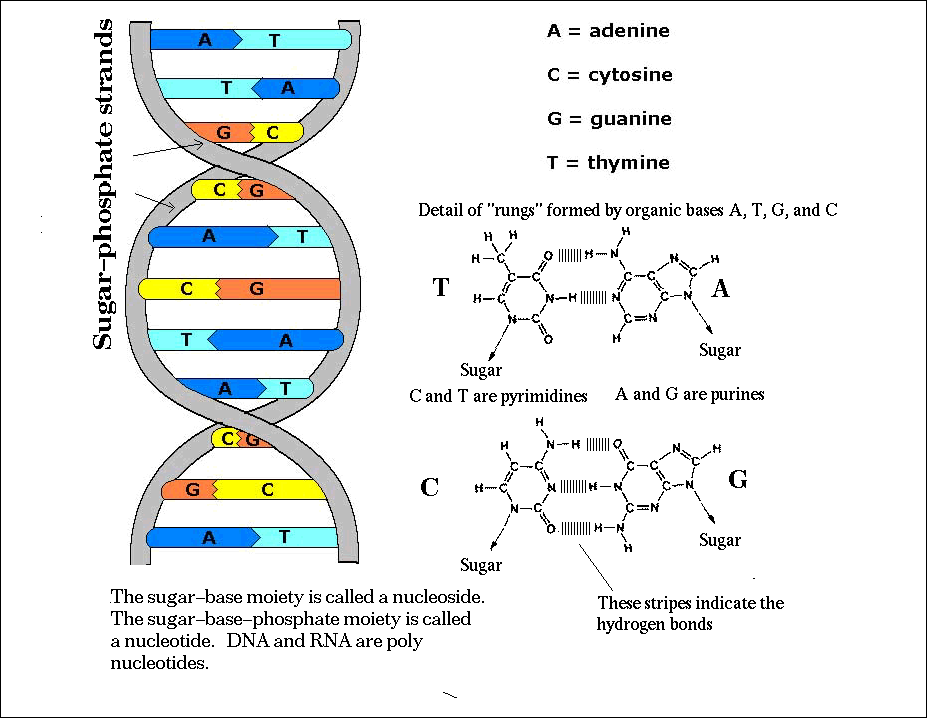
dna strand diagram
DNA Strands PowerPoint Template SlideModel
DNA Strands PowerPoint Template SlideModel

DNA Strands PowerPoint Template SlideModel

Chapter The Code — The Biology Primer
The Promoter Is The Sequence Of Dna That Encodes The Information About Where To Begin Transcription For Each Gene.
The Antisense Strand Of Dna Is Read By Rna Polymerase From The 3' End To The 5' End During Transcription (3' → 5').
After Rna Polymerase Binds To The Promoter, The Dna Strands Unwind, And The Polymerase Initiates Rna Synthesis At The Start Point On The Template Strand.
These Enzymes Unzip Dna Molecules By Breaking The Hydrogen Bonds That Hold The Two Strands Together.
Related Post: