What Is Template Dna
What Is Template Dna - Dna polymerase, an enzyme, recognizes each base in a template strand and matches it to the complementary base in a free nucleotide. Web a dna template strand generally refers to the strand which is used by the enzyme dna polymerases and rna polymerases to attach with the complementary bases during the process of replication of dna or at the time of transcription of rna respectively. A replication unit is any chunk of dna that is capable of being replicated — e.g. This is a good question and an important topic, but it is a complex idea to explain. The coding strand, also called the sense strand or the plus strand, is a crucial component of the dna molecule. The mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with the exception that rna contains a uracil (u) in place of the thymine (t) found in dna. In some cases, the rna molecule itself is a finished product that serves some. Actually, the mrna strand is coded from the template strand of the dna which runs from 3' to 5' end. Fluorescent “chain terminator” nucleotides mark the ends of the fragments and allow the sequence to be determined. The addition of nucleotides occurs in the 5’ to 3’ direction. Web transcription uses one of the two exposed dna strands as a template; Web transcription is the first step in gene expression. The template strand, also referred to as the antisense strand or the minus. Depending on the promoter, either strand of dna can be used as the template strand. That is, some genes run one way, some the other. In sanger sequencing, the target dna is copied many times, making fragments of different lengths. Web transcription uses one of the two exposed dna strands as a template; Web dna sequencing is the process of determining the sequence of nucleotides (as, ts, cs, and gs) in a piece of dna. They differ only by a few properties and functions. Web. In sanger sequencing, the target dna is copied many times, making fragments of different lengths. Web dna sequencing is the process of determining the sequence of nucleotides (as, ts, cs, and gs) in a piece of dna. Dna polymerase, an enzyme, recognizes each base in a template strand and matches it to the complementary base in a free nucleotide. Alternatively,. Web note that at any place in a dna molecule, either strand may be serving as the template; A plasmid with an origin of replication (ori) is a replication unit. Web what is template dna? Web polymerase chain reaction, or pcr, is a technique to make many copies of a specific dna region in vitro (in a test tube rather. In all cases, however, rna polymerase transcribes the dna strand in its 3'→ 5' direction. The coding strand, also called the sense strand or the plus strand, is a crucial component of the dna molecule. Translation is the process of using an mrna molecule as a template to produce a protein. Depending on the promoter, either strand of dna can. Web note that at any place in a dna molecule, either strand may be serving as the template; Web dna concentrations of templates. Web to prepare the dna template, add the forward and reverse oligos to a microcentrifuge tube at a final concentration of 2 μm ts oligo and 2.2 μm nts oligo in buffer containing 20 mm tris ph. First, it is important to clarify the structure of dna, and how it is used in the cell. For pcr products, a quick method for estimating the proper/minimal concentration is the following: This process takes us from one starting molecule to two daughter molecules, with each newly formed double helix containing one new and one old strand. When a cell. Web dna concentrations of templates. Web the template strand serves as the dna template for transcription, which is the first step of gene expression. A plasmid with an origin of replication (ori) is a replication unit. Web transcription uses one of the two exposed dna strands as a template; They differ only by a few properties and functions. Pcr relies on a thermostable dna polymerase, taq polymerase, and requires dna primers designed specifically for the dna region of interest. Web transcription is the first step in gene expression. Web both coding and template strands are distinct strands of a dna structure. This process takes us from one starting molecule to two daughter molecules, with each newly formed double. First, it is important to clarify the structure of dna, and how it is used in the cell. Translation is the process of using an mrna molecule as a template to produce a protein. Depending on the promoter, either strand of dna can be used as the template strand. Fluorescent “chain terminator” nucleotides mark the ends of the fragments and. Standardize your dna concentration to 0.2 to 0.4 µg/µl for 4 to 6 kb plasmids, increase the concentration proportionally for larger plasmids, and reduce it for smaller plasmids. Web a short segment of dna is “unzipped,” so that the two strands in the segment are separated to serve as templates for new dna. Depending on the promoter, either strand of dna can be used as the template strand. For pcr products, a quick method for estimating the proper/minimal concentration is the following: The enzyme then catalyzes the formation of an ester bond between the 5′ phosphate. Transcription is performed by enzymes called rna polymerases, which link nucleotides to form an rna strand (using a dna strand as a. Web the configuration of the dna molecule is highly stable, allowing it to act as a template for the replication of new dna molecules, as well as for the production (transcription) of the related rna (ribonucleic acid) molecule.a segment of dna that codes for the cell’s synthesis of a specific protein is called a gene. Web the replication complex is the group of proteins that help synthesize the new dna strands. Web both coding and template strands are distinct strands of a dna structure. Web transcription uses one of the two exposed dna strands as a template; In some cases, the rna molecule itself is a finished product that serves some. The mrna product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other dna strand, called the nontemplate strand, with the exception that rna contains a uracil (u) in place of the thymine (t) found in dna. Alternatively, this can also mean a region of dna that is replicated together. The presence of tris and salt in the annealing buffer facilitates correct annealing of the template dnas). Guide to research techniques in neuroscience (third edition), 2022 related terms: The coding strand is the dna strand whose base sequence is similar to its primary transcript (rna).
DNA Strands PowerPoint Template SlideModel
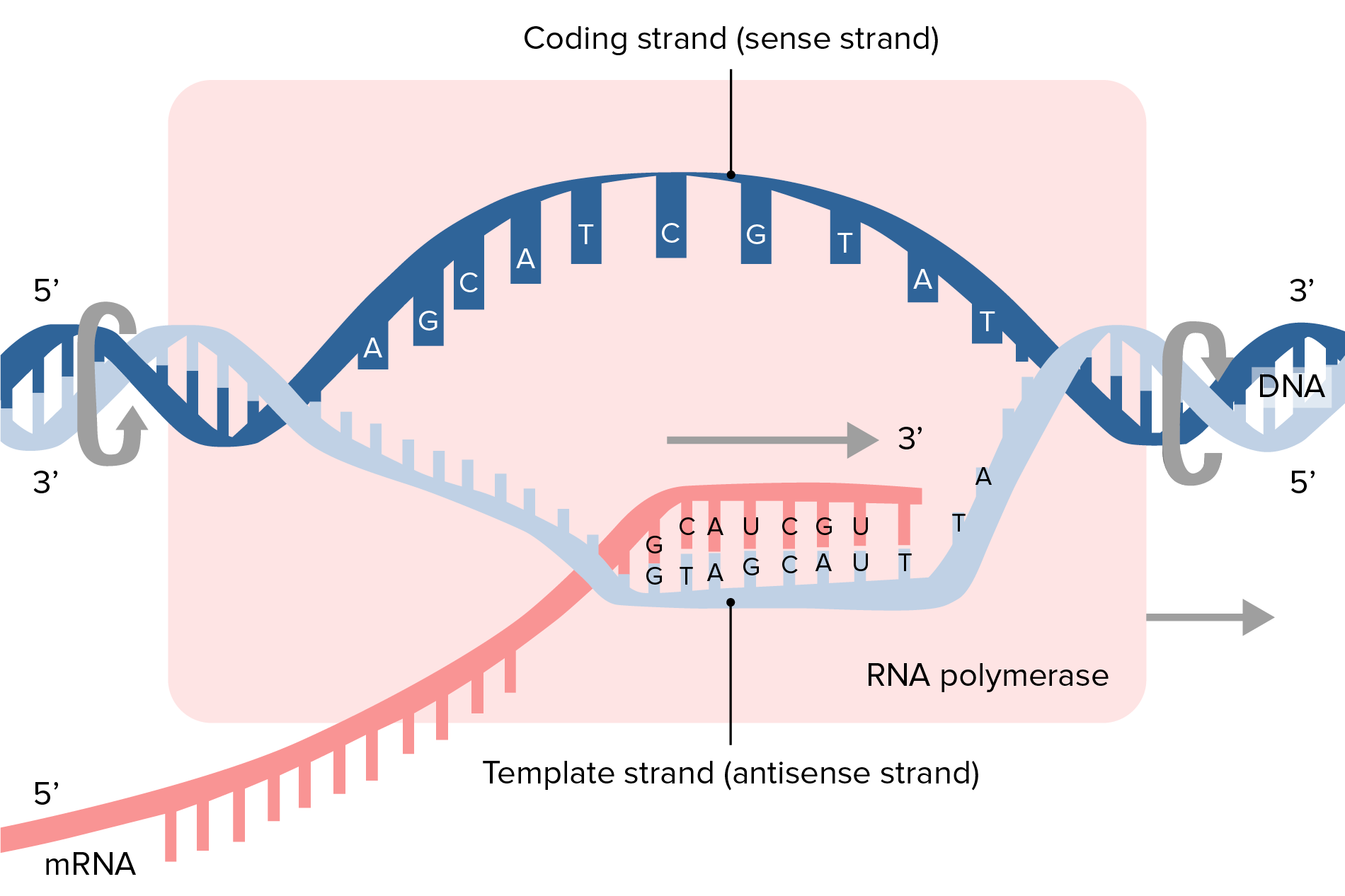
Synthesis Of An Rna Molecule From A Dna Template
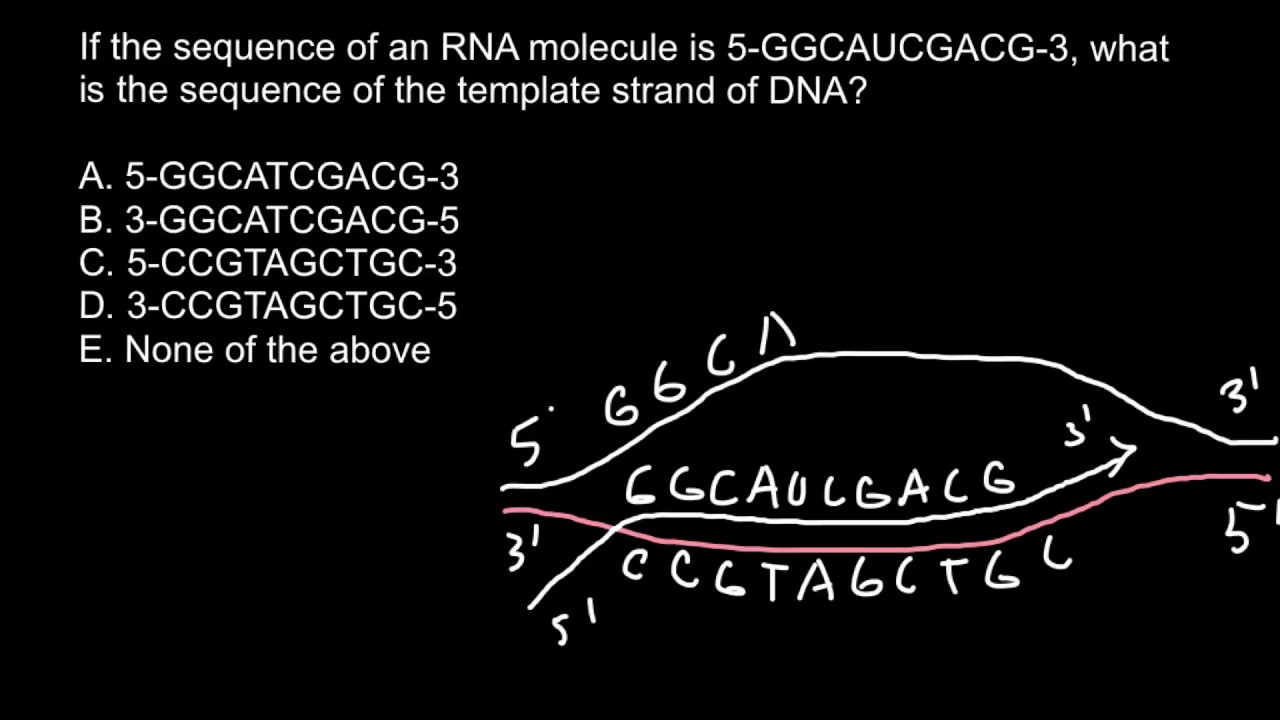
How to find sequence of the template strand of DNA YouTube
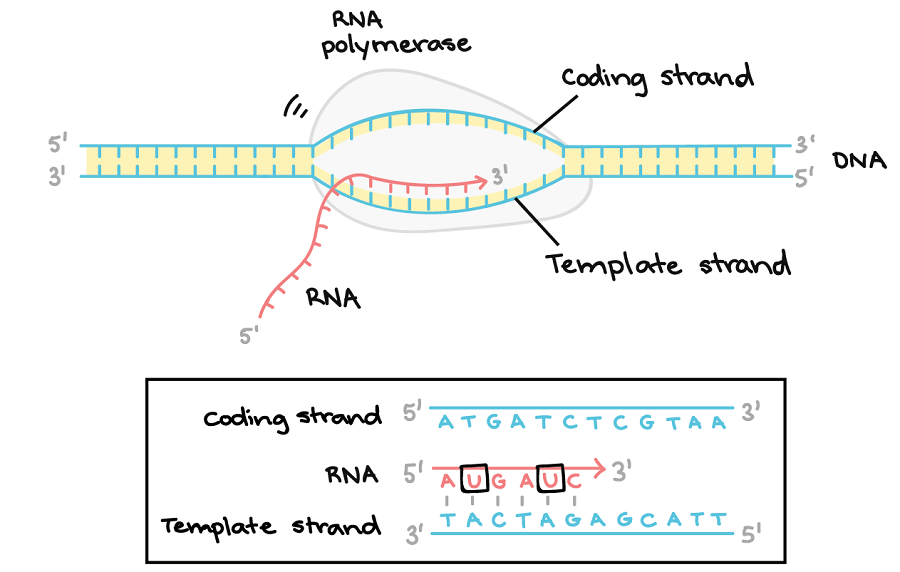
DNA Transcription (RNA Synthesis) Article, Diagrams and Video
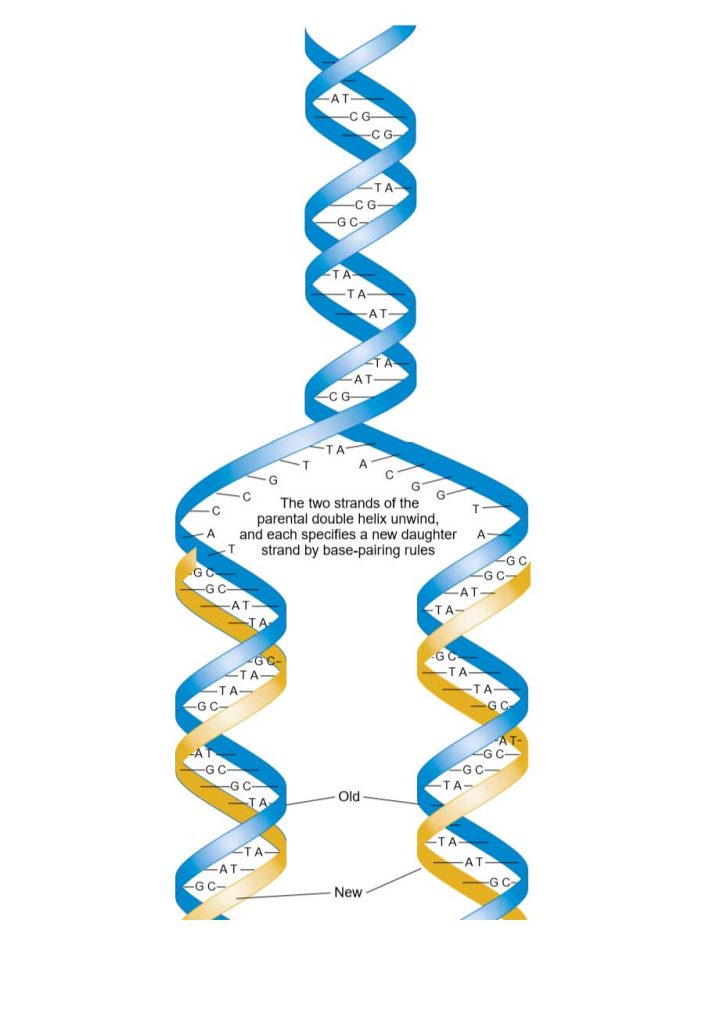
DNA Replication Study Solutions
DNA Strands PowerPoint Template SlideModel

DNA Definition, Discovery, Function, Bases, Facts, & Structure

DNA Structure & DNA Replication Biology Online Tutorial

Chapter The Code — The Biology Primer
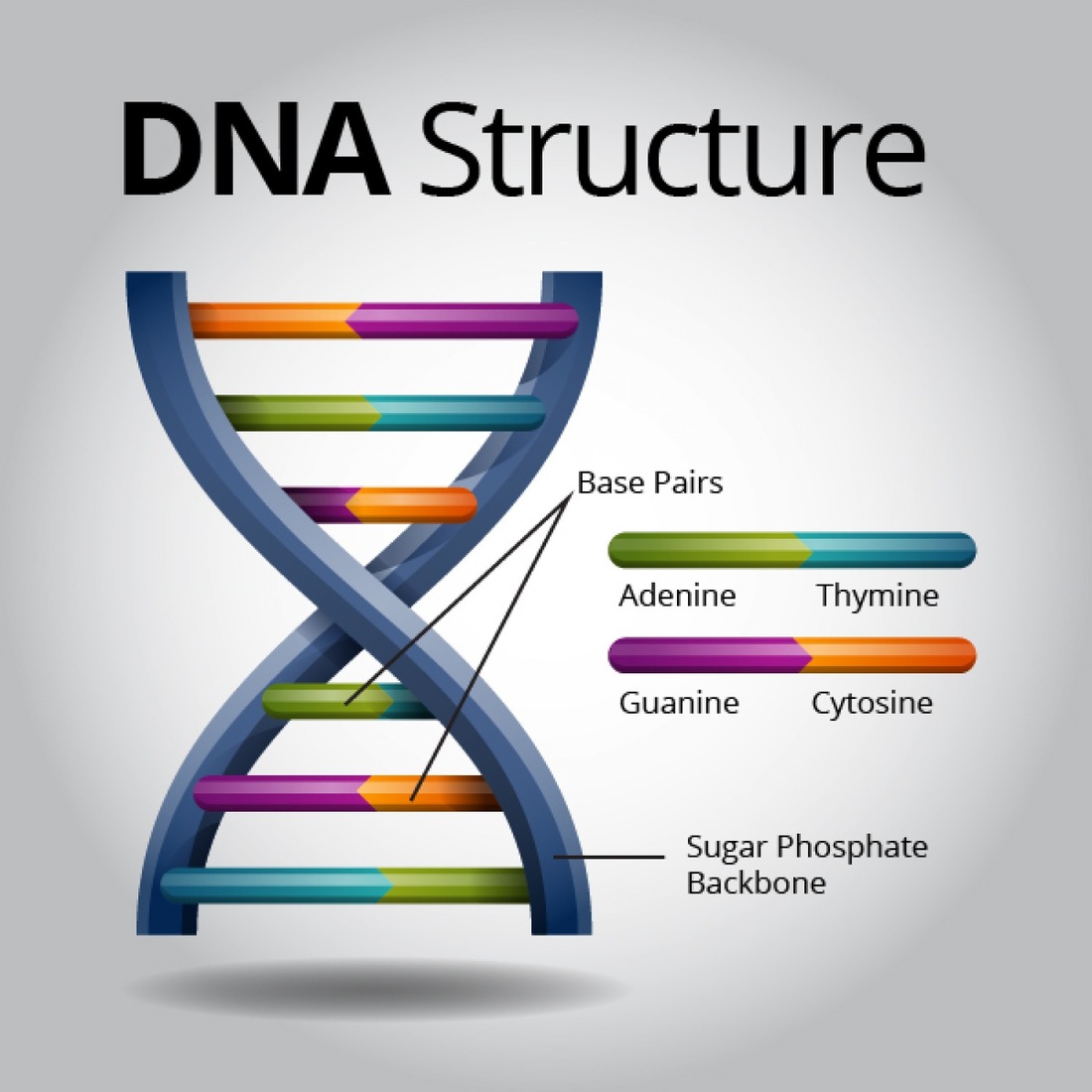
DNA AP Biology Portfolio
The Promoter Is The Sequence Of Dna That Encodes The Information About Where To Begin Transcription For Each Gene.
Pcr Relies On A Thermostable Dna Polymerase, Taq Polymerase, And Requires Dna Primers Designed Specifically For The Dna Region Of Interest.
It Causes Dna Melting Of The Dna Template By Disrupting The Hydrogen Bonds Between.
Web Transcription Is The First Step In Gene Expression.
Related Post: