Template Dna In Pcr
Template Dna In Pcr - This technique involves 0.1 m potassium hydroxide treatment at 100°c for 10 min followed by. They identify the portion of dna to be multiplied and provide a starting place for replication. The only information needed for this fragment to be replicated is the sequence of two short regions of nucleotides (the subunits of dna) at either end of the region of interest. The amplification is achieved by thermostable taq dna polymerase enzyme. For pcr templates, it is important that the product is purified away from the pcr reactants, especially the primers, as these can cause high background in the sequencing reaction. As an initial guide, spectrophotometric and molar conversion values for different nucleic acid templates are listed below. Deoxynucleoside triphosphates (dntps) required cofactor: Web the integral component is the template dna —i.e., the dna that contains the region to be copied, such as a gene. The ingredients are assembled in a tube, along with cofactors needed by the enzyme, and are put through repeated cycles of heating and cooling that allow dna to be synthesized. Web the polymerase chain reaction (pcr) is a method to rapidly amplify sequences of dna. Web pcr is incredibly sensitive and repeatable when analysing pure dna samples. They identify the portion of dna to be multiplied and provide a starting place for replication. Genomic dna, plasmid dna, cdna or purified pcr products can be used as template dna in pcr. The source of dna can include genomic dna (gdna), complementary dna (cdna) or plasmids. For. As little as one dna molecule can serve as a template. Genomic dna, plasmid dna, cdna or purified pcr products can be used as template dna in pcr. Web how does pcr work? Web standard pcr reagents include a set of appropriate primers for the desired target gene or dna segment to be amplified, dna polymerase, a buffer for the. Design with gc content of between 35 and 65%. Limit length of amplicon to about 140 base pairs. This is the biological sample you want to amplify dna from. For pcr templates, it is important that the product is purified away from the pcr reactants, especially the primers, as these can cause high background in the sequencing reaction. Web the. Spectrophotometric conversions for nucleic acid templates. Dna from a variety of sources may be used as the supplier of the dna template for 3 basic steps of the polymerase chain reaction. Web how does pcr work? During a typical pcr, template dna (containing the region of interest) is mixed with deoxynucleotides (dntps), a dna polymerase and primers. That enables all. Web the integral component is the template dna —i.e., the dna that contains the region to be copied, such as a gene. During a typical pcr, template dna (containing the region of interest) is mixed with deoxynucleotides (dntps), a dna polymerase and primers. *absorbance at 260 nm = 1. Web generally, no more than 1 ug of template dna should. *absorbance at 260 nm = 1. This is the stand of dna the taq polymerase is going to use for amplification. This is the enzyme that is in charge of replicating dna. That enables all the necessary steps for dpcr—compartmentalizing, thermal cycling, and data acquisition—to be conducted on a single instrument.the dpcr. For pcr templates, it is important that the. Web the polymerase chain reaction (pcr) is a biochemical technology in molecular biology used to amplify a single, or a few copies, of a piece of dna across several orders of magnitude, generating thousands to millions of copies of a particular dna sequence. This technique involves 0.1 m potassium hydroxide treatment at 100°c for 10 min followed by. Genomic dna,. The only information needed for this fragment to be replicated is the sequence of two short regions of nucleotides (the subunits of dna) at either end of the region of interest. Molar conversions for nucleic acid templates. Dna from a variety of sources may be used as the supplier of the dna template for 3 basic steps of the polymerase. During a typical pcr, template dna (containing the region of interest) is mixed with deoxynucleotides (dntps), a dna polymerase and primers. Dna from a variety of sources may be used as the supplier of the dna template for 3 basic steps of the polymerase chain reaction. The source of dna can include genomic dna (gdna), complementary dna (cdna) or plasmids.. Web pcr is incredibly sensitive and repeatable when analysing pure dna samples. Molar conversions for nucleic acid templates. Keep primer’s melting temperature within 2°c. This is the biological sample you want to amplify dna from. Web the polymerase chain reaction ( pcr) is a method widely used to make millions to billions of copies of a specific dna sample rapidly,. The amplification is achieved by thermostable taq dna polymerase enzyme. Web the polymerase chain reaction ( pcr) is a method widely used to make millions to billions of copies of a specific dna sample rapidly, allowing scientists to amplify a very small sample of dna (or a part of it) sufficiently to enable detailed study. The ingredients are assembled in a tube, along with cofactors needed by the enzyme, and are put through repeated cycles of heating and cooling that allow dna to be synthesized. Short strands of dna that adhere to the target segment. Web then, to perform pcr, the dna template that contains the target is added to a tube that contains primers, free nucleotides, and an enzyme called dna polymerase, and the mixture is placed in a pcr. Genomic dna, plasmid dna, cdna or purified pcr products can be used as template dna in pcr. Web the polymerase chain reaction (pcr) is a biochemical technology in molecular biology used to amplify a single, or a few copies, of a piece of dna across several orders of magnitude, generating thousands to millions of copies of a particular dna sequence. They identify the portion of dna to be multiplied and provide a starting place for replication. Design with gc content of between 35 and 65%. Web the polymerase chain reaction (pcr) is a method to rapidly amplify sequences of dna. Pcr primers are designed as pairs, referred to as forward and reverse primers. Web a standard polymerase chain reaction (pcr) is an in vitro method that allows a single, short region of a dna molecule (single gene perhaps) to be copied multiple times by taq polymerase. Web generally, no more than 1 ug of template dna should be used per pcr reaction. From a single copy of dna (the template), a researcher can create thousands of identical copies using a simple set of reagents and a basic heating and cooling. As an initial guide, spectrophotometric and molar conversion values for different nucleic acid templates are listed below. Spectrophotometric conversions for nucleic acid templates.
Overview of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Template DNA strands

Visualizing and Characterizing DNA, RNA, and Protein Microbiology
Setting up for Success How Do I Ensure I Have the Right Template for

Template Dna In Pcr
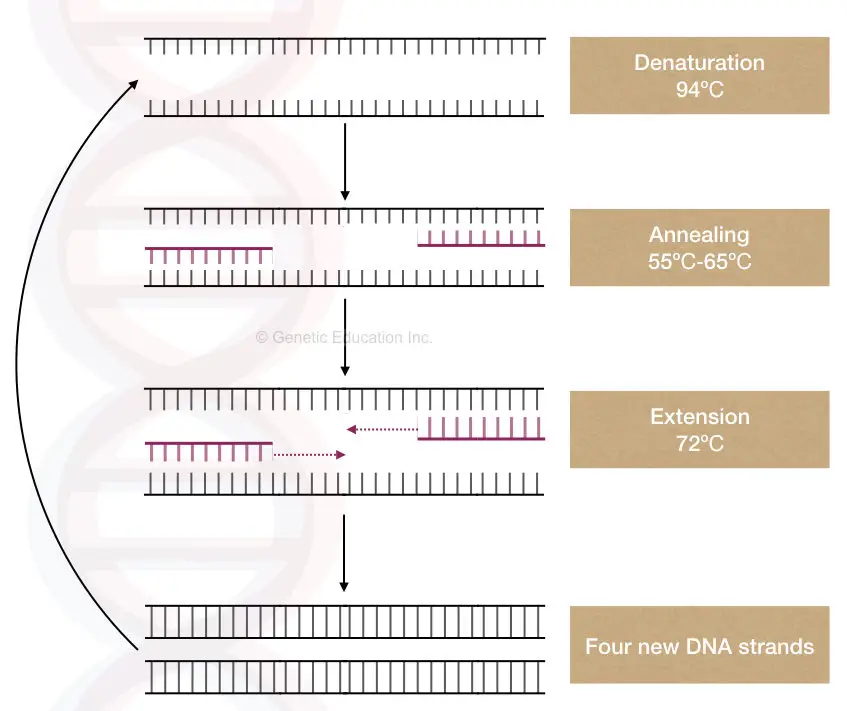
What are the properties of PCR (template) DNA?

Schematic representation of overlap extension PCR. Two DNA fragments
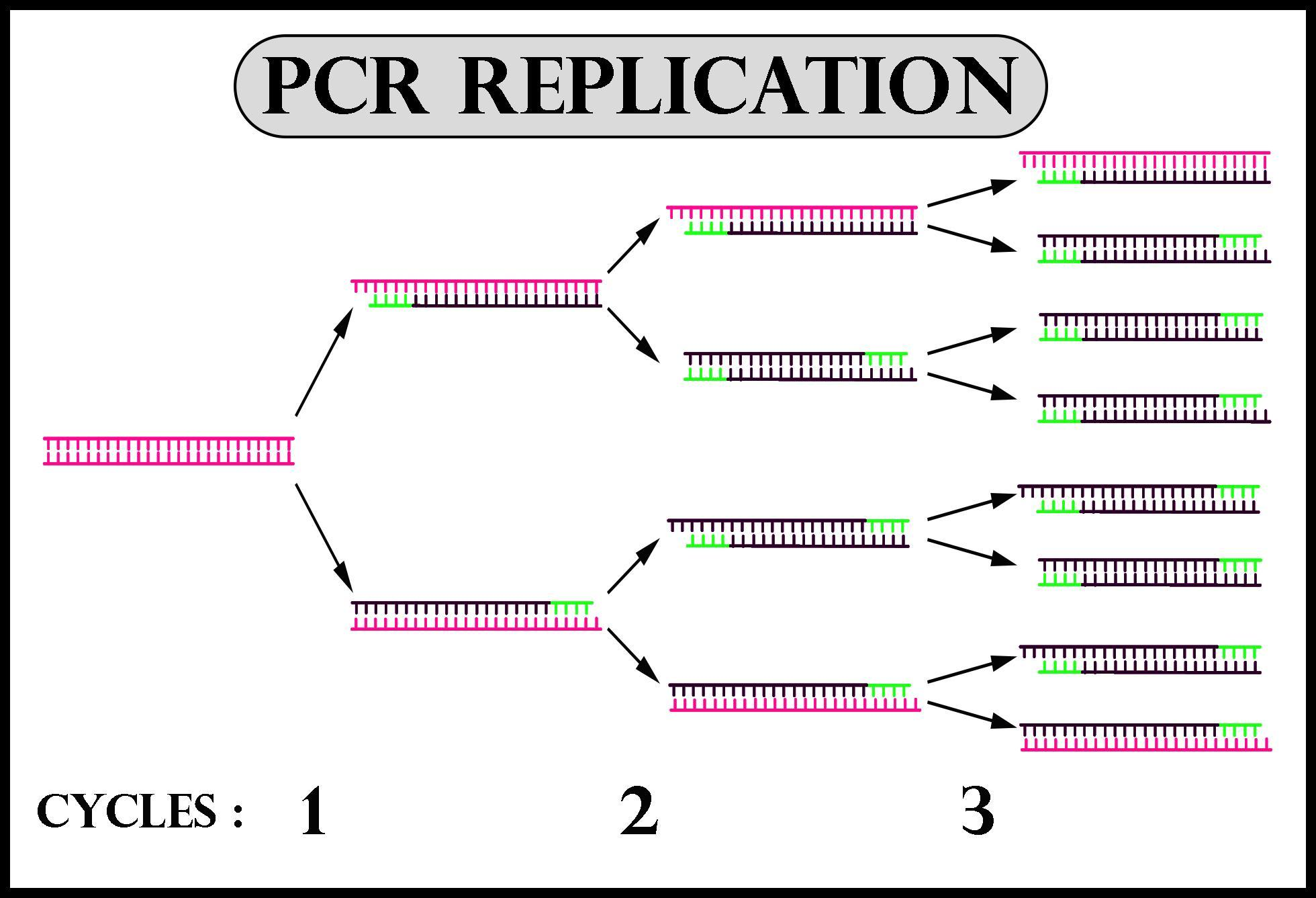
Template Dna Pcr

Template Dna Function In Pcr

What Is The Template Of The Pcr

DNA synthesis by ivTRT strategy. Schematic of plasmid or PCR product
Dna From A Variety Of Sources May Be Used As The Supplier Of The Dna Template For 3 Basic Steps Of The Polymerase Chain Reaction.
This Is The Enzyme That Is In Charge Of Replicating Dna.
This Is The Stand Of Dna The Taq Polymerase Is Going To Use For Amplification.
Web The Polymerase Chain Reaction (Pcr) Is A Laboratory Nucleic Acid Amplification Technique Used To Denature And Renature Short Segments Of Deoxyribonucleic Acid (Dna) Or Ribonucleic Acid (Rna) Sequences Using Dna Polymerase I Enzyme, An Isolate From Thermus Aquaticus, Known As Taq Dna.
Related Post: