Template Strand Of Dna
Template Strand Of Dna - Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. 24k views 10 years ago. New dna is made by enzymes called dna polymerases, which require a template and a primer (starter) and synthesize dna in the 5' to 3' direction. Web only one of the two dna strands serves as a template for transcription. Initiation of protein synthesis p. Initiation, elongation, and termination, which are aided by several enzymes. The other dna strand is referred to as the coding strand. Each new double strand consists of one parental strand and one new daughter strand. It is complementary to the coding strand of dna for the target gene. Memory anchors and partner content. The four ribonucleotide triphosphates (rntps) are atp, gtp, utp, and ctp. Replication creates identical dna strands, while transcription converts dna into messenger rna (mrna). Web position of the template and coding strands during transcription. Web dsrna generation mechanisms during ivt. Visit byju’s biology for more interesting topics. Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. New dna is made by enzymes called dna polymerases, which require a template and a primer (starter) and synthesize dna in the 5' to 3' direction. Web the template strand of dna is the strand that is used during transcription to produce rna. When referring to dna transcription, the coding strand. Difference between coding strand and template strand. This is known as semiconservative. Paul sims explains and works out how to start with a template strand of dna, transcribe it to mrna and. Web only one strand of dna is used as a template by enzymes called rna polymerases; Web only one of the two dna strands serves as a template. Web at this point, rna polymerase begins moving down the dna template strand in the 3' to 5' direction, and as it does so, it strings together complementary nucleotides. Each strand in the double helix acts as a template for synthesis of a new, complementary strand. The four ribonucleotide triphosphates (rntps) are atp, gtp, utp, and ctp. Visit byju’s biology. Replication produces two identical dna double helices, each with one new and one old strand. A dna template strand generally refers to the strand which is used by the enzyme dna polymerases and rna polymerases to attach with the complementary bases during the process of replication of dna or at the time of transcription of rna respectively. In eukaryotes, the. A dna template strand generally refers to the strand which is used by the enzyme dna polymerases and rna polymerases to attach with the complementary bases during the process of replication of dna or at the time of transcription of rna respectively. Web at this point, rna polymerase begins moving down the dna template strand in the 3' to 5'. Replication creates identical dna strands, while transcription converts dna into messenger rna (mrna). Memory anchors and partner content. Web what is dna template strand? Each new double strand consists of one parental strand and one new daughter strand. The new strand will be complementary to the parental or “old” strand. Web at this point, rna polymerase begins moving down the dna template strand in the 3' to 5' direction, and as it does so, it strings together complementary nucleotides. Rna is synthesized by using the template strand of dna as a guide for complementary base pairing. One strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary. New dna is made by enzymes called dna polymerases, which require a template and a primer (starter) and synthesize dna in the 5' to 3' direction. Initiation, elongation, and termination, which are aided by several enzymes. Web at this point, rna polymerase begins moving down the dna template strand in the 3' to 5' direction, and as it does so,. Rna is synthesized from 5' to 3'. This is because its base sequence is identical to the synthesised mrna, except for the replacement of thiamine bases with uracil. Web position of the template and coding strands during transcription. Web the model for dna replication suggests that the two strands of the double helix separate during replication, and each strand serves. An investigator is studying the transcription of dna in a mouse model. Given a dna sequence alone, you can annotate open reading frames (orfs) in order to identify the coding strand, with the caveat that not all orfs are genes. One strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary rna transcript. The new strand will be complementary to the parental or “old” strand. Paul sims explains and works out how to start with a template strand of dna, transcribe it to mrna and. Web only one strand of dna is used as a template by enzymes called rna polymerases; This is known as semiconservative. Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. Replication creates identical dna strands, while transcription converts dna into messenger rna (mrna). Web only one of the two dna strands serves as a template for transcription. Web at this point, rna polymerase begins moving down the dna template strand in the 3' to 5' direction, and as it does so, it strings together complementary nucleotides. Translation then decodes mrna into amino acids, forming proteins essential for life functions. Dna replication in eukaryotes occurs in three stages: Initiation of protein synthesis p. New dna is made by enzymes called dna polymerases, which require a template and a primer (starter) and synthesize dna in the 5' to 3' direction. The four ribonucleotide triphosphates (rntps) are atp, gtp, utp, and ctp.
Replication Britannica

DNA Strands PowerPoint Template SlideModel

DNA Strands PowerPoint Template SlideModel

DNA Strands PowerPoint Template SlideModel

DNA Strands Template Download & Edit PowerSlides™
DNA Strands PowerPoint Template SlideModel
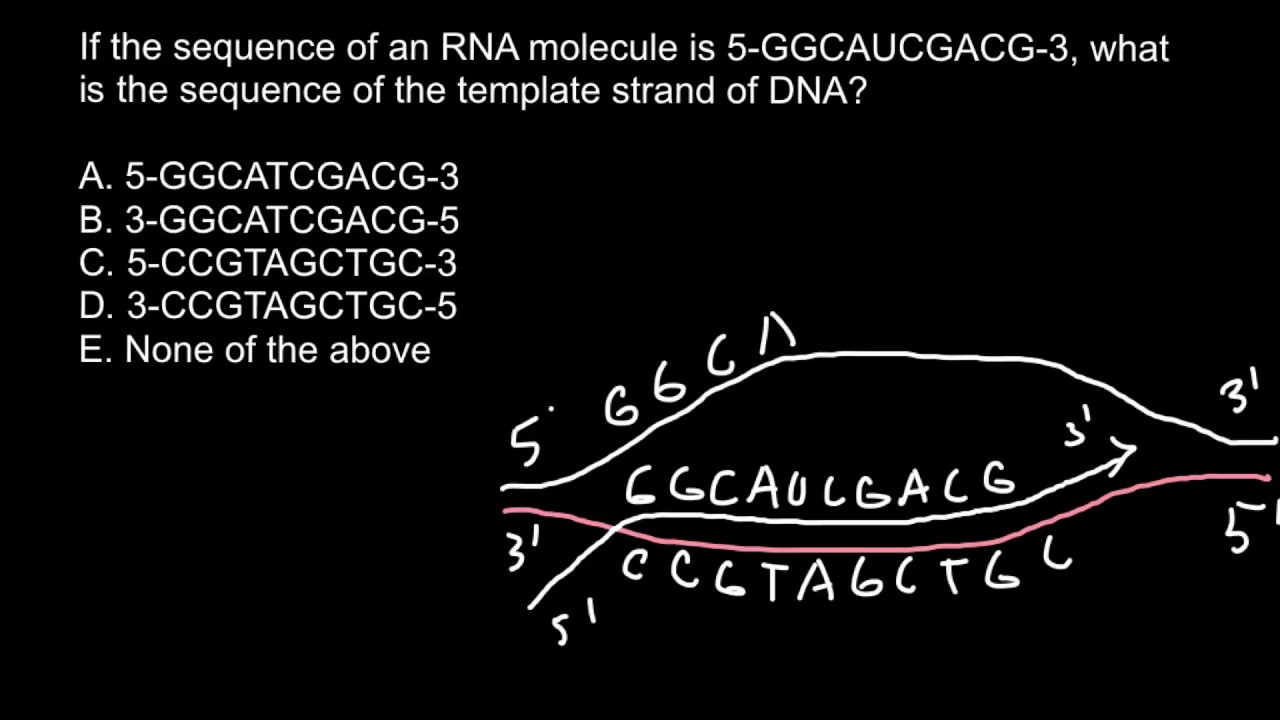
How to find sequence of the template strand of DNA YouTube

DNA Strands PowerPoint Template SlideModel

Chapter The Code — The Biology Primer
DNA Strands PowerPoint Template SlideModel
Difference Between Coding Strand And Template Strand.
Web The Model For Dna Replication Suggests That The Two Strands Of The Double Helix Separate During Replication, And Each Strand Serves As A Template From Which The New Complementary Strand Is Copied.
Rna Polymerases Do Not Need Primers To Begin Transcription.
This Template Strand Is Called The Noncoding Strand.
Related Post: